Healthy soil is the foundation of the food system. It produces healthy crops that Inturn nourishes human food need. To increase food production inorder to meet the population demands, the soil must be kept healthy and productive.
Soil health is defined as the continued capacity of soil to function as a vital living ecosystem that sustains plants, animals, and humans. That is, the soil is in good physical, chemical and biological condition. It is characterized by properties such as tilth, aggregation and microbial activity which are subjective to measurement.
For a soil to be considered healthy, there must be interaction between all soil components (living and non-living), that is, microbiota, plants and animals. A soil can be said to be healthy in terms of eco-system functioning but not healthy in performing the function of crop production or human nutrition directly. Furthermore, A soil rich in organic carbon and nutrients ( considered as high quality soil) may not be healthy soil especially when it causes injury to crops or support large parasite population.
Soil health focuses on the biotic factor of the soil. When there is a deterioration of soil health, the vital functioning part of the soil is lost. Such functioning part of the soil include: the parts that provide physical support, water and essential nutrients required for plant growth, regulation of water flow in the environment, and Elimination of harmful effects by contaminants by means of physical, chemical and biological processes.
Soil health is affected by farming practices that disturb the natural soil processes and nutrient cycle (that is, release and uptake of nutrients). Farmers need to adhere to soil health principles and systems that include no-till, cover cropping, crop rotation, increase soil organic matter, control erosion and improving microbial activities inorder to keep the soil healthy . Hence, these effects would help increase water infiltration, reduce leaching, improve soil structure and texture, improving wildlife and pollinator habitat and bring about better harvest, higher profit and better yields.

IMPORTANCE OF SOIL HEALTH TO AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTION
1. A healthy soil provides nutrients and habitat to living soil organisms
2. It raduces runoff and erosion
3. The rich organic matter helps bind soil particles together into aggregates
4. Healthy soil improves water holding capacity of the soil
5. It improves soil porosity etc.
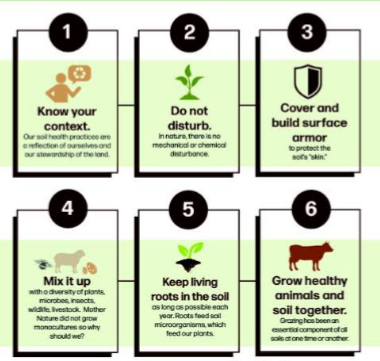
FACTORS TO CONSIDER TO CALL A SOIL HEALTH SOIL
To determine if a soil is healthy, several factors are put to consideration by farmers and scientists . They measure the number of microorganisms present in the soil, How much nutrients are in the soil, How well does the soil retain water during drought, How much carbon can the soil sequester from the atmosphere? etc. For a soil to be considered healthy, various microscopic and large organisms must teem up to provide and convert the dead and decaying matter and minerals to form plant nutrients. The following factors are used to determine the healthiness of a soil
1. The soil has many living organisms in it such as earthworms, beetles, unseen microscopic organisms
2. It is rich in organic matter
3. It is rich in plant nutrients which are in available form
4. It is deep enough for plant roots to grow properly
5. It has a mixture of fine clay particles with coarse sand and silt particles
6. It contains lumps and clumps of different sizes
7. The surface does not seal after rain.
The following factors enhances soil health :
1. Conservation agricultural practices like no tillage or minimum tillage
2. Planting of cover crops
3. Crop rotation practices
4. Fallowing
5. Well managed crop-livestock system
SOIL HEALTH INDICATORS USED TO ASSESS SOIL FUNCTION
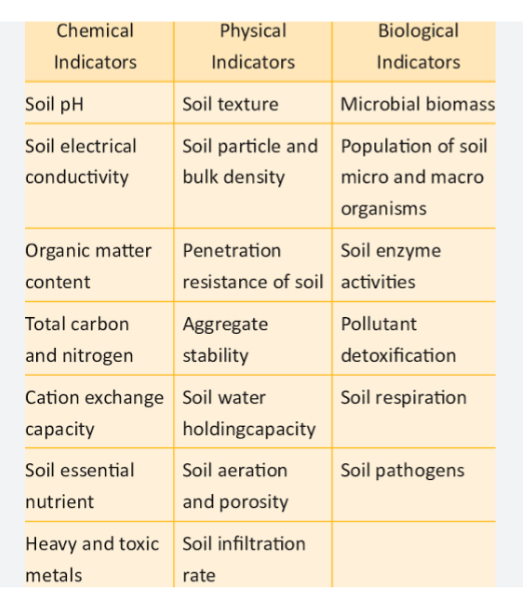
The primary indicator of soil health is Soil organic matter (SOM). Other indicators include: physical ( soil aggregate stability, infiltration and bulk density), chemical ( pH, extra table soil nutrients, N, P, K and basic cations like Ca, Mg, and K), and Biological (microbial biomass, C and mineralization of N)
Soil organic matter which is the major source of plant nutrients and soil organic carbon in the agroeco system is a major representative of soil Health .
CAUSES OF POOR SOIL HEALTH
Virgin Soils under forest, bush or grasslands have a built up of organic matter. The organic matter had been built up over many years. When farmers clear such area, they initially get very good yield. But later, as the land is ploughed, crop residues are removed, and the land left bare, plant nutrients are washed away, organic matter are eroded and the soil becomes depleted. The following are the causes of poor soil health :
I) Farming for many years and Removal of nutrients without returning the nutrients back to the soil
II) soil erosion
III) Loss of soil organic matter
IV) loss of soil life
V) break down of soil structure
VI) compaction of soil
VII) exposure of bare soil to rain and sun
EFFECT OF POOR SOIL HEALTH TO AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTION
When soil is depleted of organic matter, plant nutrients and lack the major beneficial soil microorganisms that assist in decay of residues, the soil becomes sick. The negative effects of poor soil health on agricultural production include:
I) Low crop yield
II) Need of high amount of inorganic fertilisers to produce good crop
III) stunted and dwarf crops
IV) bare soil
V) fall in crop yield year after year.
HOW TO MAKE A. SOIL HEALHTY AGAIN
1. Break hard pan to allow water sink into the soil and it will also make crop roots reach nutrients and water deeper in the soil
2. Zero tillage should be practiced. Planting basins, open planting lines or plant directly using farm tools and not machines
3. Do not remove crop residues and animals should not be allowed to graze on them. Their presence on the land helps in protecting and adding organic matter to the soil
3. Add organic matter and plant nutrients in form of compost, manures, mulching and inorganic fertilisers
4. Plant crop covers to protect the soil and produce organic matter.
5. Keep rewatering the field. Built microcatchments along field contures.
6. Practice conservation agriculture.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SOIL HEALHT AND SOIL QUALITY
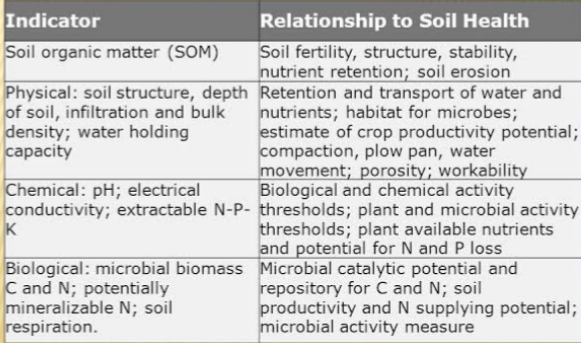
soil health and soil quality both play an important role in agriculture. The terms are often used synonymous.
Soil health describes the biological integrity of the soil community-the balance among organisms within a soil and between soil organisms and their environment.”Soil health is a description of the condition or status of a soil and may comprise multiple factors including soil quality characteristics that come together to create an environment for soil life. These factors may include soil structure, organic matter, and the diversity or population of soil micro- and macro-fauna. Soil texture and soil fertility are examples of characteristics that enhance soil health .
Soil quality is a term that we use when we talk about the physical attributes of soil. Physical attributes include: color. It can also be used to describe more complex soil characteristics such as soil organic matter, nutrient amounts, soil structure, etc. These attributes can all be influenced by management practices and have the capability to enhance or diminish soil health.
Soil quality is related to soil functions while soil health concept view soil as a finite and dynamic living resource.
Indicators of soil quality include soil physical quality, chemical fertility, organic matter, soil morphology and soil macro fauna that support plant growth.

