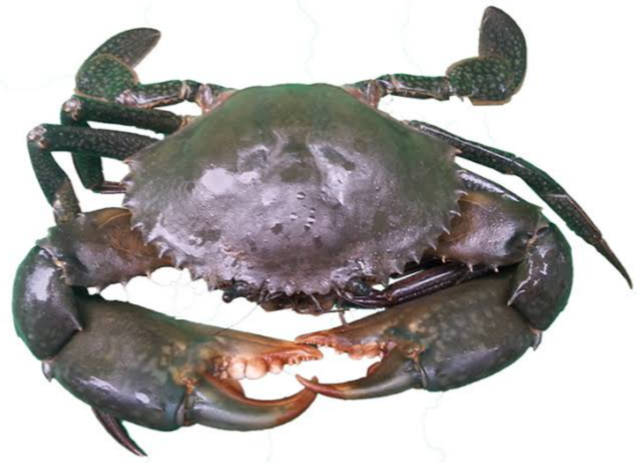

The crab farming is a rapidly growing sector with production increasing in many countries around the world. For example, Mud Crab farming has gained popularity in Asian countries where It is integrated with prawn and milk fish farming.
Crab farming is a system of preserving or protecting crabs by keeping them in salt water pen where they are fattened for market. They have huge demand in international market. March 9th marks the National Crab Meat Day. There are about 7,000 crab species all over the world. They belong to members of the kingdom animalia and subphyllum called crustaceans.
They can be found in all oceans and in fresh water. Some live on land beside water bodies. Some species live in burrows in the sand or mud. Others live within the shells of oysters or mussels (E.g hermits crab) . They possess a hard covering known as the exoskeleton which protect the internal organs. They possess five pairs of legs. The first pair has large pinching claws that help with feeding and defense. The last pair are broader and flattened to serve as paddles for crabs that swim. This swimming legs are called pleopods. They walk sideways with their four walking legs. They breathe with the aid of gills and they possess two large eyes extend from the head on movable stalks located above two pairs of antennas. The mouth is on the underside of the head.
Crabs are scavengers, meaning they eat dead or decaying material. Some feed on vegetable matter, and others eat small living animals.
Crabs are gonochoric animals. Meaning they have two sexes “female and male. Male crabs mate with the female to fertilize the eggs in her body. All female crabs do return to the water to lay eggs. The eggs are carried on the female’s body until they hatch to form a larva called zoea. Between 12 to 15 days, the zoea will moult four times and develop to form a megalopa. By this time, it would have developed claws. Few days later, it will moult to form a juvenile crab. After which it develops to form an adult crab.
HEALTH BENEFITS OF CRAB
1. CRABS TASTE DELICIOUS . They are healthy to eat and rich in many essential nutrients like protein, vitamins and minerals.
2. SOURCE OF PROTEIN : Crab meat is a healthy source of protein and energy. But it is low in saturated fat compared to animal meat.
3. BOOSTS MENTAL ACTIVITY : Crab meat is rich in essential vitamins and minerals like selenium, vitamin B2, copper and OMEGA-3 fatty acids. These nutrients help improve brain functioning.
4. The nutrients in crab meat help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation,
5. PROMOTES BONE HEALTH : Crab meat is rich in phosphorus. This helps to- build strong, healthy teeth and bones.
6. IMPROVES HEART HEALTH : Crab is low in fat but a good source of Omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, and protein, all of which help lower cholesterol level. This helps reduce the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
7. PREVENT CELL DAMAGE : Crab is rich in selenium. This essential mineral is an antioxidant which prevent cell damage from free radicals, it also boosts immune system. –
8. The Selenium in crab meat is important in proper thyroid function. It is important for controlling the speed of body metabolism, growth, and many other bodily functions. In infants, it is critical for brain development.
9. INCREASES BLOOD CIRCULATION : CRAB meat is a good source of copper. Copper helps the body to absorb iron, which improves red blood cell production. This improves circulation of blood and promote healing after injuries and illnesses.
10. TREATMENT OF DIABETICS : Crabs are rich in chromium, which helps insulin to metabolize sugar, and thereby lowers the blood glucose levels in the body.
11. TREATMENT OF CANCER : Selenium (an anti-oxidant) helps in destroying the carcinogenic effects of cadmium, mercury and arsenic on cells which can result to tumors. Higher levels of selenium in the blood lead to lower rates of cancer.
12. DETECTION OF MENINGITIS : lysate an extract from the blue blood of the horse-shoe crab is used for detection of spinal meningitis and for fighting cancer.
STARTING CRAB FARMING

CRAB farming requires the best management practices inorder to reap the gains brought forth. Some of the management practices include proper water management, right soil selection, soil and water temperature and pond design.
Some farms uses high technology to farm crabs without using ponds. Vertical farms which uses recirculatory aquaculture systems are employed in such cases.
CRABs can be raised from eggs untill they reach market size. Mud crabs are harvested from the wild and eggs and sperms are collected from both the female and male adult crabs. Artificial fertilisation is carried out and the eggs hatched into baby crabs.
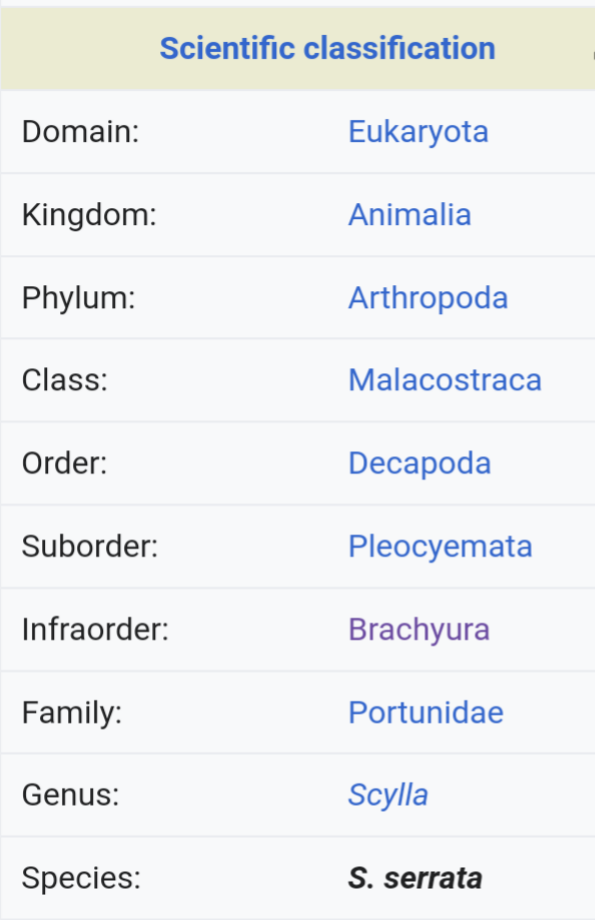
1. HATCHERY: The male and female mud crabs are caught from the wild. At the hatchery, the male is cut open and sperms sac which is whitish in colour is extracted from it . The female is also cut open and eggs are extracted from the opening. The eggs are orange in colour.
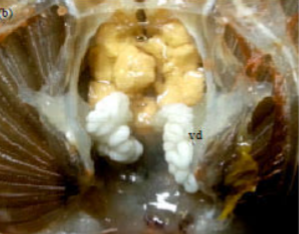
The sperms sac containing sperms is gently cut open to release the sperms. A little brackish water should be added to the sperms to make them move. The sperms are then introduced to the eggs and both stirred gently to increase the chances of all the eggs to be fertilized. When the colour of the eggs change slightly, this means the eggs are fertilized. Then it should be gently poured in a bowl of brackish water to hatch.
After hatching, the young larva called zoea emerges and are moved to the pre-nursery structures.
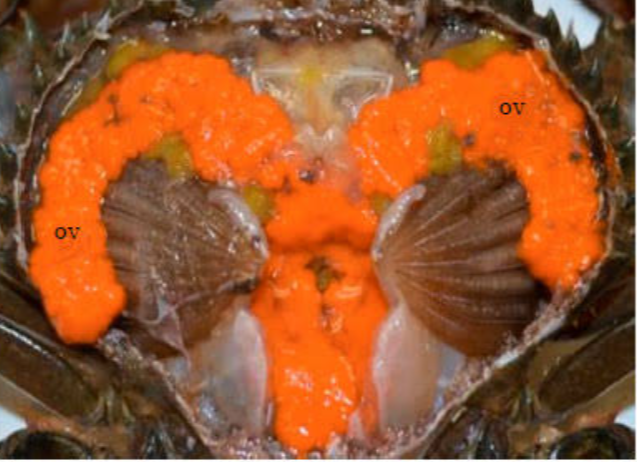
2. PRE NURSERY GROWING OF YOUNG CRAB: Young crabs are grown between 5 to 6 months until they attain table size. At one day old, they are usually lighter and float on water. As they continually moult to shed their exoskeleton, they grow bigger. At 3 to 4 months, the young crabs can be moved from the nursery and be introduced into the pond. The pond size usually range from 0.5 to 2 hectares. If the pond is small, fencing should be done.
3. POST-NURSERY: Between 6 to 7 month, the crabs would have reached marketable size compared to those picked in their natural habitat which reaches marketable size between 18 to 24 months. Vertical crab farming system have being designed to overcome the challenges of mud pond farming system. Such challenges include high mortality rate caused by cannibalism and disease infections. Vertical farming boxes are used to house each crab saving land spaces usage and water recirculation systems are employed.

MUD CRAB FARMING
Mud crabs (Scylla serrata) are also called mangrove crabs. They are found in the estuaries and mangroves of Africa, Australia, and Asia. They are caught and consumed globally making them an important species for both commercial and sustainable farming. The farm has become a viable option for those looking to enter the seafood industry.
Mud crab farming is the process of raising mud crabs in a controlled environment such as ponds and tanks. They are raised for commercial harvesting and for sale. Freshwater and salt water can be used to raise mud crabs.
The major gaol of mud crab farming is to produce high quality, safe and sustainable mud crabs products for consumers
SPECIES OF MUD CRABS
There are four species of mud crabs, but only two are found in West Africa. Scylla serrata the green mud crab and Scylla olivacea the brown mud crab. The green mud crabs have a larger body size than the brown mud crab

Other difference between the green mud crabs and the brown mud crabs include
1. ELBOW: The green mud crab has more than one prominent sharp spine while the brown mud crab has one blunt or no spines
2. LOBES: The green mud crab have long narrow lobes between the eyes while brown mud crabs have short broad lobes between the eyes
3. CLAWS: Green mud crabs have large and distinct claw spines which are dark green or purple coloured. While brown mud crabs have reduced or blunt claw spine which are light brown or orange in colour.
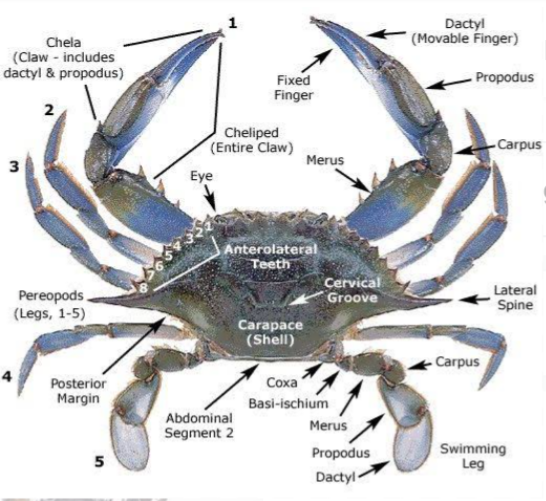
IMPORTANCE OF MUD CRAB FARMING
1. ECONOMIC BENEFITS : Mud crab farming can provide income to farmers and provide job for local community dwellers especially those living at the coastal regions.
2. SUSTAINABILITY: The pressure on wild meat and wild mud crabs can be reduced through raising of mud crabs in a controlled environment. High population of mud crabs can be raised through controlled environment. This will help ensure the sustainable of the species.
3. IMPROVE LIVELIHOOD : Mud crabs provide a source of income and food security. People at the coastal regions engage in fish farming as a source of livelihood also can engage in mud crab farming to increase their income level
4. FOOD SECURITY: Mud crab farming provides a reliable and steady source of food especially proteinous meat with low cholesterol level. This helps to meet the growing demand for mud crab and reduce the dependency on wild stocks
5. ALL YEAR PRODUCTION : Mud crab farming is an all year production enterprise especially when raised in vertical farms.
6. INTEGRATED FARMING : Mud crab can be integrated with other farming such as prawn and milk fish farming, and even crop farming etc. Resources from one enterprise can be used for the other enterprise. For example, water from the pond can be used to irrigate crop farm and produce from the farm like veges can be fed to the crabs.
7. SHORT GROWTH PERIOD: In vertical mud crab farming and fattening systems, the crabs are turned into profitable meat within a short period of time (less than a year)
8. ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY SYSTEM: Mud crab pond system and use of vertical farming for mud crabs require no chemical usage. Water used in the vertical farms can be recycled and reuse again. Therefore, no or less pollution comes from such farming practices.
9. ORGANIC FEEDS ARE FED: So far no chemicals are used in mud crab farming, every activities of feeding is purely organic. Natural food materials such as fish and veges are fed to them.
10. NOT COST EFFECTIVE : farmers do not need a huge budget to start crab farming. It can be done on a small scale while the farmer continue to build on it or expand the enterprise.
11. LOW LABOUR COST: The Labour cost is very low. A labourer May be employed just to feed and assist in harvesting the crabs.
HOW TO RAISE MUD CRABS
There are two systems used in raising mud crabs
1. Grow out systems
2. Fattening system

GROW OUT SYSTEM
This type of farming system is pond based. The young crabs are reared for a period of 5 to 6 months till they reach market size and weight. The pond size is between 500 m2 to 20000m2. Feed fed to the crabs include rotten fish, birds, meats pieces from slaughter house. The ponds depending on the size should be fenced to prevent predators.
FATTENING SYSTEM.
The fattening system involves raising soft shelled crabs for some period of time until their exoskeleton become hardened up. The price of hard shelled crabs are five times higher than price of soft shelled crabs.
The period of farming crabs in this system is shorter compared to that in the grow out system
To fatten crabs, two systems are involved
a) fattening in pond
b) fattening in pens or cages.
FATTENING IN PONDS
Small ponds of size between 250 to 2000 m2 and 1to 1.5m depth are used for fattening crabs. The pond are fenced, drained, sun dried and limed before stocking with crabs.
FATTENING IN PENS OR CAGES

In this fattening system, crabs are raised in shallow Marine water ways or in large ponds or tanks. Series of Pens, floating net cages and bamboo cages can be arranged along the Marine water ways to fatten the crabs. In the cage, 10 crabs per square meters should be placed in the cage.
CRAB FOOD
Some Crabs are herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and scavengers. Most of them are carnivores and scavengers. They feed on artificial pelletized feed which are available in feed stores. The feed on the sinking pelletized feed and not the floating type. They can also be feed with rotten fish, pieces of meat from abarteur, vegetables, etc
LIMITATIONS OF CRAB FARMING
1. Poor water quality management is a factor that leads to high mortality of crabs.
2. Poor system design
3. Moulting of exoskeleton is the way crabs grow bigger. As they moult, the young are vulnerable to attack by hard shelled crabs, fishes and birds etc. These would thereby reducing the density of crabs in the pond
4. Care should be taken so that there is no crack or holes around the sluice area and bunds of the pool so that the crabs do not escape in the case of pond system.
5. Disease outbreak
6. Limited access to high quality seed stock
7. High cost of inputs such as feeds and equipment
In conclusion, mud crab farming industry is a dynamic and growing sector with significant potential for expansion and development. Countries all over the world should now cue in adopting this farming practices so as to reduce the pressure on wild meat source to supply their protein needs and embrace the sustainability of mud crab farming
