
In the past, food shortage where either inappropriate or non-existent in Africa and other continent in the world. This was so due to low population of communities coupled with simple eating habits and other factors. Enough food where available for the majority, improved medical and health care where in place and this reduce death rate. Also, more people engage in farming and non farming employments. With the reduced proportion of farmer population, extra food were still in place to feed the non farming population and sufficient for export. Policies were favorable to farming to solve local problems. These policies were used to monitor, supervise, direct and creat pace setting in the Agricultural sector. With this, more problems resurfaced and where tackled. But ,this policies gradually began to disrupt the progress and erode the confidence within the Agricultural sector. These coupled with high cost of Agricultural inputs like fertilizers and other agrochemicals etc, lack of processing and storage facilities, adamant habit of some farmers to adopt new farming technologies etc. The Agricultural production potential became non sustainable, hunger increased and population of young fellows who can input their knowledge and energy to improve the Agricultural sector reduced drastically. Hence, food insecurity became a challenging factor which the whole world began to battle with.
FOOD SECURITY: Food security means that all people, at all times, have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food that meets their food preferences and dietary needs for an active and healthy life. Food insecurity on the other hand is when people cannot access the food they need to live their fullest lives. That is, when people do not have enough to eat and do not know where their next meal will come from. This is a huge problem all over the world. Even the so called developed continents are faced with food insecurity. For example, the United States have over 44 million people, including 13 million children, experience food insecurity annually. Africa, Asia and other continents are no exemption. Most of the people in countries faced with food insecurity takes to charitable food sector for support, some turn to beggers for arms, some theft for survival etc.
It is important to note that food insecurity does not necessarily cause hunger but hunger is a possible outcome of food insecurity
CAUSES OF FOOD INSECURITY
Food insecurity may be influenced by a number of factors. Such factors include: income, employment, race/ethnicity, and disability.
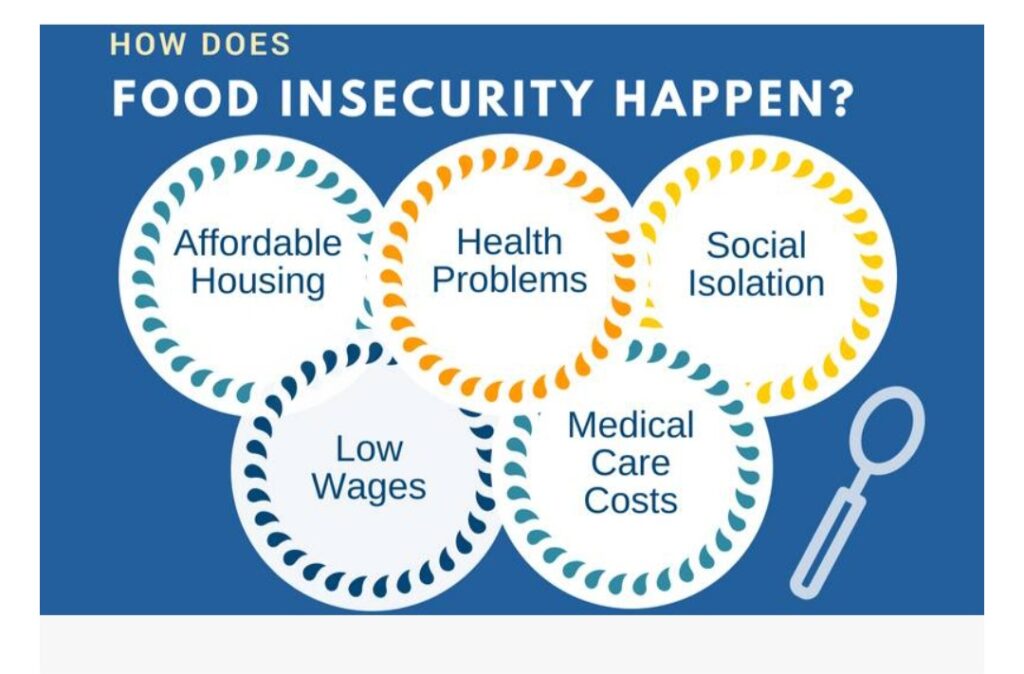
1. LACK OF AFFORDABLE HOUSING / SHELTER : To afford renting an apartment can be expensive. Even if care is taken in spending money and savings, paying for an house rent may still be expensive. With this, it may be hard to have enough left over to buy food. Most tenants will have to split their little income to pay their exorbitant bills and not clear it at once. Therefore, the little apportioned for food might or may not be enough to cater for them and their family. 2. POVERTY AND UNEMPLOYMENT : Unemployment can negatively affect a household’s food security status. A lot of people in countries all over the world are unemployed. Some are low-income earners who find it difficult to meet basic household food needs. Most of these people depend on family members, friends and borrowing to survive. Some do not even have people to rely upon to have a meal on their table. Such People with no or little money cannot afford to buy food regularly, provide good shelter to protect them, purchase good clothing and even have assess to good medical care. They depend on unbalanced or unhealthy food. Even if such food are available, they will have to purchase it at a high prices. 3. CHRONIC HEALTH CONDITIONS : Health is wealth. People with sound health are the only one that can work or even search for jobs if they get any. Or even become self employed. People with long-term health issue, will find it difficult to work and earn enough money. Even if they earn enough money, most of it will be spent on medical bills and purchase of drugs rather than sufficient food to fill their belly. 4. RACISM AND DISCRIMINATION : Lot of racial discrimination is all over the world today. Racism and discrimination can occur among marginalized communities, including people of different skin colour, LGTBQ individuals, and even those with disabilities. They face higher risk of food insecurity due to systemic discrimination and poverty. A lot of white skinned men do not want to have any affair with black men and vice versa, likewise some ethnic groups. Also, a lot of physically challenged or disabled individuals are indiscriminately rejected among the physically fit individuals. Such individuals faces a lot of challenges to survive. Disabled adults may not be giving employment opportunities and health care-related expenses may be difficult to come by. 5. OTHER FACTORS: Other factors apart from the above can also result to food insecurity. People with steady income and access to affordable housing can also experience setback that leads to food insecurity. This can be as a result of job loss, low wage jobs, medical emergency, natural disaster or family crisis.

EFFECTS OF FOOD INSECURITY. Food insecurity have serious consequences on people’s health and well-being. Some of the consequences include: 1. PHYSICAL HEALTH. Food insecurity may lead to people experiencing malnutrition and chronic conditions like heart disease, brain damage, obesity, cancer and diabetes etc. When human’s diet is not balanced, they are exposed to various types of malnurish diseases. 2. MENTAL HEALTH. Food insecurity can also lead to mental disorder such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder and stress. When human brain cells are not well fed with nutrients especially for a long time, the above metal disorder (brain damage) may occur. 3. SOCIAL WELL-BEING : Human’s basic needs include food, shelter, clothing etc. When these basic needs are not met, social isolation, stigma, and shame becomes inevitable. 4. SCHOOL AND WORK : Food is needed to make the brain cells function properly. When people do not have assess to enough food or balanced meal, they may experience difficulty in concentrating, lack energy, or miss school and work due to illness. Children of unemployed may not have assess to education and even if they do, the education might be of low quality compared to children of the employed. Most of these children assist their parents in hacking instead of going to school. This is very common among African households.
HOW TO IMPROVE FOOD SECURITY. Food security can be improved based on the following ways: Reducing food waste, enhancing infrastructure and promoting more efficient production techniques . These are key ways to improve food security. 1. FOOD WASTAGE AND FOOD LOSSES: It has being estimated that food losses and wastage per year worth billions of dollars. These losses and wastage start from the farm to the market place. Food losses and wastage are caused by lack of processing facilities, storage facilities, pest and disease attack, inefficient preparation methods, crop failures, incorrect storage of food and consumer preferences (e.g. slightly rotten fruit or oddly shaped vegetables) etc. Food wastage can be reduced by introducing improved methods of food preparation. One example is the use of vegetable trimmings in soups. Food loss can be reduced by improving storage, processing and packaging techniques. The Packaging should indicates the manufacturing date, expiry date, content of the food and storage processes. 2. IMPROVING INFRASTRUCTURE AND PRODUCTION TECHNIQUES : Upgrading the infrastructure to modern one and practicing mechanized farming also ensures that less food is lost and improves food security. Sufficient number of people and machines must be available for farming activities such as sowing, use of agrochemicals, weeding and harvesting. Crops must be properly protected and cared for against weeds, diseases and pests. Storage facilities must be in place, minimal farm processing facilities must be available if not quickly transported to factories or market and good transport to markets or end users must be available. 3. DIVERSIFICATION OF AGRICULTURAL PRACTICES. Practicing Monoculture or monocropping has lots of disadvantages. It can degrade the soil, crop become more vulnerable to diseases and pests, soil nutrients are lost and it can lead to crop fails. Farmers need to diversify to other crops by practicing crop rotation, mixed cropping, introduce new components on their farm like fishery, poultry and ruminants so that waste from one components can be used for production of the other component. This reduces cost of production and guide against failure of components. 4. COMBATING CLIMATE CHANGE. The effects of climate change include Droughts, wildfire, rise in sea level and floods etc. Wildfire, drought and flood can cause crop failure. The carbon dioxide from the wildfire can bring about green house gas effect. Thus, causing food insecurity. Putting measures in place to combat climate change can help reduce crop failures. Also, good agricultural practices such as Afforestation etc can make a positive contribution to a better climate. Crops absorb CO², thus, reduce the amount of greenhouse gases. Working crop residues into the soil later on makes a double contribution to a better climate. 5. WAR AND CONFLICT : Wars, conflicts and social insecurity can also lead to food insecurity. In some parts of the world where there is war, farmers will not be able to go to farms and lots of agricultural production chains will be destroyed. Such as factors, farms, and market places will be destroyed. The inhabitants who are concerned about survival and safety, will be protecting themself and their family from the threat of being harmed. In Nigeria for example, where the cattle rearers (fulani) are not in good terms with the farmers, people find it dangerous to go to their farms because of threats of being killed. Lots of farm produce are destroyed by the animals.

PILLARS OF FOOD SECURITY. At the World Summit on Food Security in 2009, four pillars or elements or indicators of food security were mentioned and defined. The four pillars include: availability, access, utilisation and stability. These pillars can be used for the improvement of food security. They were described using the following keys, so as to achieve food security ; availability, accessibility, adequacy, acceptability and agency, and the framework .
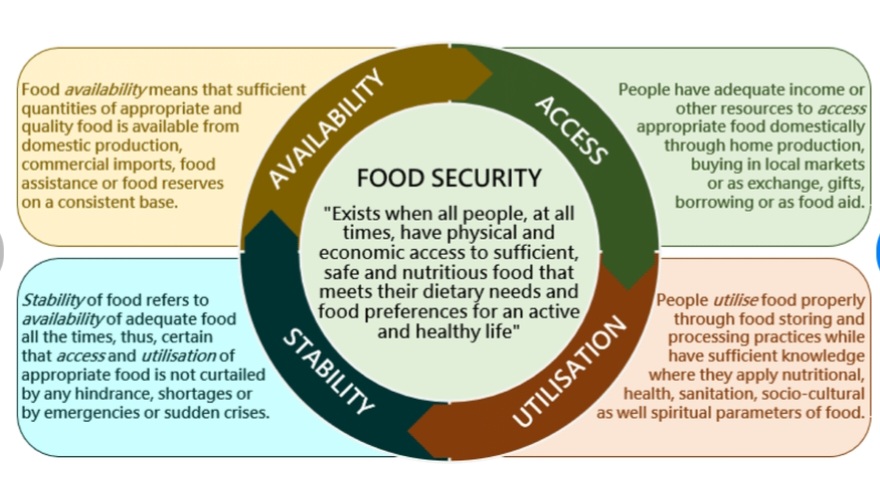
1. AVAILABILITY. The world agricultural produce producers are sufficient enough to produce food that will feed all the world’s population. These food can only be made available through production and distribution. The production areas must be large enough to grow food. But these crops and livestock farming are also facing some production constraints which lead to food insecurity. Such constraints include: competition with other land usage such as housing and industrialization, growing world population, emerging plant and animal pests and diseases, degraded soil fertility, increasing use of land for fuel rather than food, and lack of attention to agricultural research and development. After production, the produce must be stored and processed. Also, the produce can also be affected by pest damage and if some are not properly dried, they develop mold. The longer the produce stays in the store, the faster its quality deteriorates. After processing, the food must be transported and distributed. All of these processes ensures that food wastage is reduced to the bearest minimum.
2. ACCESS TO FOOD
The national production of food and it’s distribution is not a major problem but how do country’s have access to the food from the global market through foreign exchange to feed her citizens.
Most household produce their own food in their backyard farm and those they find it difficult to produce are purchase by their household members at the market place. These are ways citizens gain access to food. These ways of accessing food is of two different aspects.
i. DIRECT ACCESS : which refers to the ability of people to grow and harvest food for themselves. ii. ECONOMIC ACCESS : which refers to the ability to buy food. The availability of food does not mean that people have access to it. The availability of money in people’s pocket determines how much food they would buy and the amount and type that would be served on their table. Other factors that have impact on food accessibility include: Income and education levels, Gender, household population, sociocultural factors and consumer preference etc
3. UTILISATION
The fact that food is available does not mean the food is of good quality. The quantity and quality of food must qualify each other for better satisfaction of the needy. The food must also be safe.
Nutritional standards exist for the actual nutritional needs of men, women, boys, and girls of different ages and life phases (that is, pregnant women). This nutritional needs must be met so that they can develop and grow properly. When this nutritional standards are not met, diseases are inevitable.
The food must also be stored and prepared in an hygienic way. It must be balanced and of good quality. Poor quality food can have a negative impact on a person’s health.
4. STABILITY
Finally, the stability of access to healthy food also plays an important role in food security. This stability can be jeopardised by natural phenomena . However, wars, unemployment and inequality can also lead to food insecurity.
Food security is important for social stability and health. It ensures that all individuals within a country and the whole world have access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and preferences at all time.
The following three pillars ; food supplies/availability, access, and utilization must be consistent and reliable to ensure food stability. All households should have access to nutritious and balanced food. They should have access to food at all time as a consequence of sudden shocks (e.g. an economic or climatic crisis) or cyclical events (e.g. seasonal food ).
Food stability are ensured by stability of prices and government policies, constant physical access to markets and availability of agricultural inputs to all.
The stability of food can be jeopardized by natural phenomenon such as war, conflicts, inequality, and unemployments. All these can lead to food insecurity.
In conclusion, as the world’s population is growing rapidly on daily basis. This growing population’s needs especially food need must also increase. People will not only need access to sufficient nutritious food but sufficient nutritious food that is balanced.
More sustainable and efficient farming practices will be needed to produce enough quality food to meet human’s needs.
