Global warming result in climate change. Atimes, these two phrases are used interchangeably, but they are different. Climate change refers to changes in weather patterns and growing seasons around the world. It also refers to sea level rise caused by the expansion of warmer seas and melting ice sheets and glaciers.
It is also refer to as a long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. Such shifts can be natural, due to changes in the sun’s activity or large volcanic eruptions or due to human activities which is the main driver of climate change, primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas.
Global warming causes climate change, which poses a serious threat to life on Earth in the forms of widespread flooding and extreme weather. When the earth’s temperature rises due to global warming, heavy rainfall, severe droughts, heatwaves and cyclone will occur. When a huge amount of carbon gasses such as Carbon dioxide, Methane, and Chloro-Fluorocarbon are emitted into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gasses in factories, industries and through the vehicles, it creates the greenhouse effect in which carbon gasses which are greenhouse gas are emitted and they act like a blanket /sheet wrapped around the Earth, trapping the sun’s heat and raising the earths temperatures. Thus, causing green house effect
The main greenhouse gases that are causing climate change include carbon dioxide and methane. These gases are from using gasoline for driving a car or burning coal for heating a building and decomposition of waste at dump sites. Clearing land and cutting down forests can also release carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. Agriculture, oil and gas operations are major sources of methane emissions. Energy, industry, transport, buildings, agriculture and land use are among the main sectors causing greenhouse gases.
CONSEQUENCES OF CLIMATE CHANGE
The consequences of climate change now include, among others, intense droughts, water scarcity, severe wildfires, rising sea levels, flooding, melting polar ice, catastrophic storms and declining biodiversity.
Climate change can affect human health, ability to grow food, housing, safety and work. Other impacts such as saltwater intrusion has negatively affected human and their communities causing them to relocate. Adverse effect of droughts has resulted to famine. Therefore, in the future, it has being predicted that the number of people that will be displaced by weather-related events and hunger will rise.

CAUSES AND EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE
A. FOSSIL FUELS : Fossil fuels are the largest and primary contributor to the greenhouse gas emissions that cause climate change, which poses many risks to all forms of life on Earth. When fossil fuels burn, they release greenhouse gases – mostly carbon dioxide (CO2). This traps extra energy in the atmosphere near the Earth’s surface, causing the planet to heat up.
Since the start of the Industrial Revolution – when humans started burning large amounts of fossil fuels – the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere has risen by about 50%.

B. VOLCANIC ACTIVITIES: Volcanic activity can bring about climate change in a number of ways at different timescales. Volcanoes are not the major cause of warming the earth is experiencing today. Volcanoes release carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfuric gases and other greenhouse gases when they erupt, which can lead to climate warming especially if the input of CO2 to the atmosphere is sufficiently large.
In addition, when eruption occurs, sulfuric gases are converted to sulfate aerosols which is a sub-micron droplets containing about 75 percent sulfuric acid. The production of these aerosol particles can form a cloud in the atmosphere, reducing atmospheric transparency and thus the amount of solar radiation reaching Earth’s surface and troposphere. The aerosol can remain lingering as long as three to four years in the stratosphere thereby reducing the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface, lowering temperatures in the troposphere, and changing atmospheric circulation patterns. Thus, resulting in an unusually cold over many parts of the world.
The volcanic aerosol clouds will absorb the terrestrial radiation, and scatter a significant amount of the incoming solar radiation, an effect known as “radiative forcing”, this can last from two to three years following a volcanic eruption. Thus, affecting the Earth’s radiative balance.
The effect of Volcanic eruptions only causes a short-term climate change and contribute to natural climate variability.

C. SOLAR VARIABILITY : Radiation from the Sun makes the sun the ultimate source of energy on earth. It provides all the energy that drives the Earth’s climate system. Any fuctuations in the solar output will definately affect the climate on Earth. The output from the Sun may vary and these variations may influence the Earth’s climate. The sun provides luminosity, or brightness, which increases during the day, and decrease at night, and also with season.The Sun also provides heat on earth and also provides the energy to drive atmospheric circulation.
The two factors critical for the survival of life on earth can be altered thereby bringing about climate change on earth. One of the factors is the protection provided by the Earth’s atmosphere and the second is the warmth supplied by the Sun’s radiation. Therefore, any change in the radiative output of the Sun will also affects the energy balance of the Earth’s surface and atmosphere, thereby influencing the earths climate. Changes in the solar spectrum, in particular the Ultra Violet radiation could enhance or dampen this influence, by affecting stratospheric chemistry: most importantly the balance between ozone production and destruction (each driven by radiation at different wavelengths). Also, the low lying cloud cover can increase the coverage of solar radiation from reaching the earth.
D. DEFORESTATION : Deforestation is a primary contributor to climate change and climate change affects the health of forests. Trees help improve the climate by absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. During deforestation, largest amount of carbon stores are released to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. The deforestation process can be by burning of forest biomass or cutting down of trees and decomposition of remaining plant material and soil carbon.

When trees are deforested through burning, more carbon dioxide are released into the atmosphere and there are less trees to take in the carbon dioxide and release oxygen during photosynthesis. These released and atmospheric carbon dioxide would trap heat from the sun which causes the increase in temperature which leads to global warming.
E. INTENSIVE FARMING :
Intensive farming system which is common in modern day agriculture is practiced due to increase in population to meet the high food demand of the populace. In intensive farming, farmers utilize higher amount of chemical inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, and practice mechanization which has lead to degradation of the environment. The exploitation of natural resources, poor maintenance of soil health, pollution of water bodies etc. make such intensive agricultural practice unsustainable.
Through the practice of mechanized farming, climate change had being worsened because the machines used in intensive farming are mainly powered by the burning of fossil fuels like diesel and petrol. Burning fossil fuels causes climate change because it releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere which traps heat and increases the temperature of the earth.
Also the integration of livestock or increase in livestock production in intensive farming, For example, cattle and sheep, produce large amounts of methane when digesting their food and excrete. While fertilizers produce nitrous oxide emissions. Which are green house gases causing climate change
F. WASTE DISPOSAL :
The waste sector is one of three key methane emitting sectors following agriculture and oil and gas and is responsible for about 20% of human-driven methane emissions globally.
A lot of methane gas stem from the breakdown of organic waste such as food and yard waste, kitchen wastes, as well as paper, cardboard, and wood under anaerobic (i.e., oxygen free) environment. When the solid waste brake down at landfills or dumps sites large amount of methane are released. The organics decay slowly, releasing what is commonly known as landfill gas (LFG), a combination of methane and carbon dioxide which are green house gases
In addition, the management of waste through incineration produces a lot of carbon dioxide as the waste are burnt

G. MINING : The rising demand for more minerals is associated with increase in energy needs. Metals and minerals are the raw materials used in the construction industry, transportation sector, and manufacturing of goods. When extracting mineral ore, large chunks of earth are removed with explosives or heavy machinery. Those machines run on fossil fuels that release CO2 and other pollutants into the atmosphere, while explosives produce carbon monoxide, which also contributes to global warming
H. OVERCONSUMPTION : Some of the natural resources on earth include; forest, wetlands, mountains, water bodies and land etc. Practices such as logging, agriculture, construction, mining, industrialization and development etc have led to the widespread destruction of those resources that are carbon sink and other natural resources that store carbon dioxide and prevent it from being released into the atmosphere.
The changes human make to some natural resources have direct impact on the environment by altering landscapes and harming biodiversity. Other natural resources are harvested as part of industries that cause greenhouse gas emissions and carbon emissions, accelerating global warming and climate change.
Overconsumption worsens the exploitation of these resources and result in climate breakdown and increases air pollution. It exhausts the planet’s life support systems like fresh water, and leaves materials detrimental to human health and quality of life. etc.
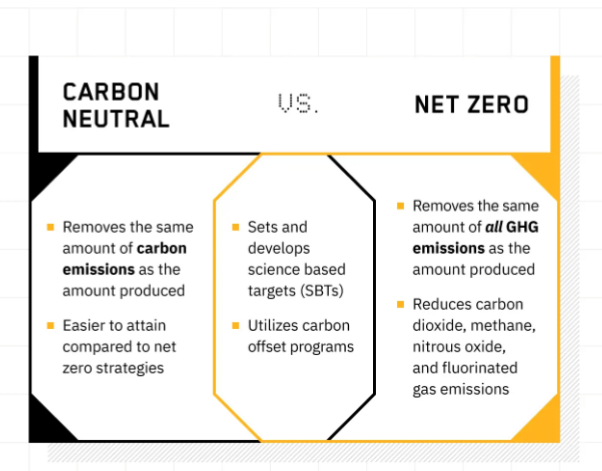
I. LACK OF NET ZERO CARBON BALANCE: Net zero refers to the balance between the amount of greenhouse gas that’s produced and the amount that’s removed from the atmosphere. It can be achieved through a combination of emission reduction and emission removal. Simply put,
Net zero means that any carbon emissions created are balanced (kind of cancelled out) by taking the same amount out of the atmosphere. So net zero will be reached when the amount of carbon emissions is not more than the amount removed from the atmosphere. But when the amount of carbon emission is very high than the amount of carbon that is removed from the atmosphere, green house effect occurs.
SOLUTIONS TO CHALLENGES OF CLIMATE CHANGE
Certain actions are needed to be emback upon to combat the challenges brought by climate change. These actions can be categorized into three. The three broad categories of action are: cutting emissions, adapting to climate impacts and financing required adjustments.
a. CUTTING EMISSIONS: Emission of gases that causes climate change can be from forest fire, smoke from exhaust pipe of vehicle, waste gases from industries, mining and burning of fossil fuel and coal etc. To overcome such gases Emission, there is need to switch the energy systems from fossil fuels usage to renewable energy sources like solar or wind energy which will reduce the emissions driving climate change.
There should be a huge declines in the use of coal, oil and gas. Thus, net zero carbon should be practiced by countries.
b. ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE: Adapting to climate consequences protects people, homes, businesses, livelihoods, infrastructure and natural ecosystems. It covers current impacts and those likely in the future. Adaptation will be required everywhere, but must be prioritized now for the most vulnerable people with the fewest resources to cope with climate hazards. The rate of return can be high. Early warning systems for disasters, for instance, save lives and property, and can deliver benefits up to 10 times the initial cost.
c. FINANCING REQUIRED ADJUSTMENTS : Climate action requires significant financial investments by governments, NGOs and other businesses to combat the challenges of climate change. But climate inaction is vastly more expensive. One critical step is for industrialized countries to fulfil their commitment to provide $100 billion a year to developing countries so they can adapt and move towards greener economies. Also, government of each countries of the world should enforce policies that will minimize carbon emission within their domain.
BENEFITS OF CLIMATE CHANGE :
Despite the challenges of threat brought by climate change, it brings about several opportunities to both developed and developing countries. Most countries are now struggling to becoming a net-zero carbon country. These are countries using energy with no carbon emissions from the product or service rendered to their populace. Such countries encourage for example their farmers to engage in wind farm generating electricity, or a battery deploying electricity rather than use of resources that produce green house gases. This involve a huge investments in new and renewable energy industries like wind, solar, and hydropower industries embacked upon by such countries. Some of the benefits such countries derive from using such zero carbon resources include : creation of millions of jobs across their country, providing more green infrastructure to meet the future demands of their populace. These Green infrastructures ( buildings) will spur low-carbon economic growth and create skilled jobs in emerging markets for decades to come. Also, climate change will be controlled through promotion of big investments in the following six key sectors: waste, renewable energy, public transportation, water, electric vehicles, and green buildings.
All these sectors need greater reforms to meet future demands and reforms require innovation and creativity. Through this, massive job will be available for young unemployed youths especially in developing countries.

