The conversion of fuel into useful energy also produce heat and many types of pollutant in the air and water. The most crusial concern in the world today is the possibility that the earth weather could be permanently changed by carbon dioxide emission from the burning of fossil fuels. These global warming has the potential to bring about devastating effects that the world has never experienced before.
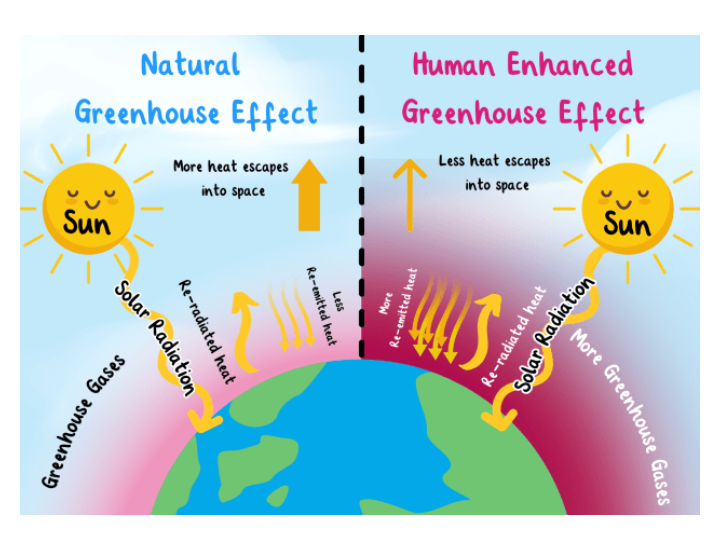
Evidence is mounting up in these century as human continues to burn fossil fuel, leveling the forest, release of some damable exhausting gases that can increase the earth temperature by atleast several degrees, thus, causing Global warming and green house gas effect.
The green house gas effect is caused by natural or man made activities which releases gases in the atmosphere that absorb certain wavelength of infra red radiation to space. Some of the man made activities include deforestation, use of vehicles, chlorofluorocarbon, industrial development, agriculture, and overpopulation. The natural causes include :volcanoes, water vapour, melting permafrost ( frozen soil that has environmental gases trapped in it for several years and is present below Earth’s surface.) and Forest fire.
Increasing carbon dioxide concentration will surely cause more heat to be trapped within the Earth’s atmosphere. There are some other green house gases that are also powerful absorbers of the heat that is emitted in thesame range of wavelength. Some of them are : methane, chlorofluorocarbons -CFC , water vapor, and, nitrous oxide.
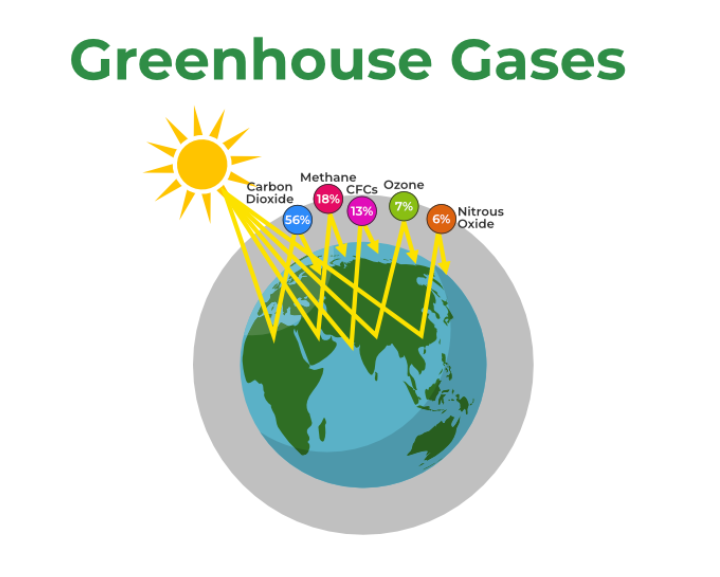
Of all these gases, carbon dioxide is the most important, both for its role in the greenhouse effect and for its role in the human economy. Although, these gases are present in small quantities, yet, they can remain in the atmosphere for several years and play thesame significant role as the carbon dioxide. These gases have different atmospheric life time, that is, carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofloro carbon – CFC and, nitrogen oxide have their atmospheric life time as 100 years, 10 years, 100years,and 170 years respectively.
Global warming is the main cause of climate change. Sometimes these phrases are used interchangeably, however, they are different. Climate change refers to changes in weather patterns and growing seasons around the world. It also refers to sea level rise caused by the expansion of warmer seas and melting ice sheets and glaciers. Global warming causes climate change, which poses a serious threat to life on Earth in the forms of widespread flooding and extreme weather. Scientists continue to study global warming and its impact on Earth.
IMPLICATION OF GLOBAL WARMING
The implication of global warming include
1. Increase global warming will be larger at the poles and this could lead to the melting of the polar ice cap thereby raising the level of the ocean by 0.3 to 7.5m. This means that the various parts of the world could be one day submerged under water. It has lead to increase in floods, tsunamis and other natural calamities.
2. The change in precipitation and stem pattern could create a shift on the productive areas of oceanography and agriculture and alter the growing season negatively.
3. A few degree warmer in temperature means that summer period may get terribly unbearable.
4. Because ocean current are usually driven by temperature differences, between that of the poles and equator. Some areas of the world especially in Europe could also become very cold due to changes in circulation patterns of the ocean.
5. It also causes damages such as increased extinction of many plant and animal species, shifts in patterns of agriculture, and rising sea levels.
6. Climate Change. It result in droughts at some places and floods at others. This climatic imbalance is the result of global warming.
7. Global warming create a favourable environment for disease causing organisms and their spread. Global warming leads to a change in the patterns of heat and humidity. This has led to the movement of mosquitoes that carry and spread diseases
OZONE DEPLETION
Ozone in the Earth’s atmosphere occurs in two separate locations and present a different concern for each region. One important contributor of ozone layer depletion is the presence of chlorofluorocarbon ( CFC). CFCs are nontoxic, nonflammable chemicals containing atoms of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine. CFCs are classified as halocarbons, a class of compounds that contain atoms of carbon and halogen atoms. It can rise to the atmosphere and get decomposed by ultraviolet radiation therefore reducing what is called a free chlorine atom which can vigorously attack the ozone thereby creating chlorine oxide and oxygen molecules. It is distorbing to note that one chlorine atom can distroy about 100,000 ozone molecules. And because of CFC are intact, they can remain in the atmosphere for 100 years thereby looking for one damage or the other to accomplish.
CFC on the other hand has some commercial application. They can be used severally as aircraft propellant or aerosols. Also as refrigerant, some as solvents, blowing agents in foam industries, and food packaging industries.
THERMAL POLLUTANT
This is defined as the addition of heat to the environment especially natural bodies of water. The greatest source of heated water is from steam electric generating station where condensing units are needed to complete the steam cycle and to improve the efficiency of the power plant. In the condenser, thermal energy is removed from the hot steam by passing cooling water through the condenser coils. The cooling water is usually taken from and then discharged into a body of water such as a lake or river.
Once there is a temperature change, one can then expect an increase in the thermal energy. Since Q=MCDT
Where
M=mass of water body
Q= heat capacity
DT= Temperature change
It shows the DT is definitely related to mass of water flowing through the condenser and the amount of heat added. Nuclear power plant and fossil power plant have different impact upon the environment but their common features is the emission of waste heat which is related to the thermal efficiency of the energy.
The thermal efficiency is the ratio of the electric energy output to the heat energy input.
£= O^e/I
Where O^e is the electric energy output
= (O^e) /(O^e +w)
“w” means waste heat
The second equation is from the energy conservation principle.
The energy input = energy output + waste heat.
Since energy was said to be conserved
“e” means thermal efficiency of the machine
£(O^e +w) =O^e
£O^e +£w=O^e
£w= O^e – £O^e
w= (O^e – £O^e) /£
“w” is the thermal pollution coefficient or waste heat
ECOLOGICAL EFFECT OF THERMAL POLLUTION
1. Decreases ability of water to hold oxygen
2. Increases rate of chemical reaction in the bodies of water
3. Changes in reproduction, behaviour and growth patterns through out the food chain
4. Long term damage and in some cases, death of the natural bodies of water
COGENERATION
This is another aspect of global warming. It is the production of both electricity and useful heat from thesame sources. That is, the useful parts of waste heats and electricity are combinely generated.
Over the past centuries, two types of Co- generation are in existence. The first generate electricity from a turbine generator and uses the exhaust gases of high pressure steam to process the steam for discrete heating. This is called the process of topping cycle.
Second procedure takes steam that have being needed for industrial process and runs it through a low pressure steam into the turbine for the generation of electricity. This process is called a bottom cycle.
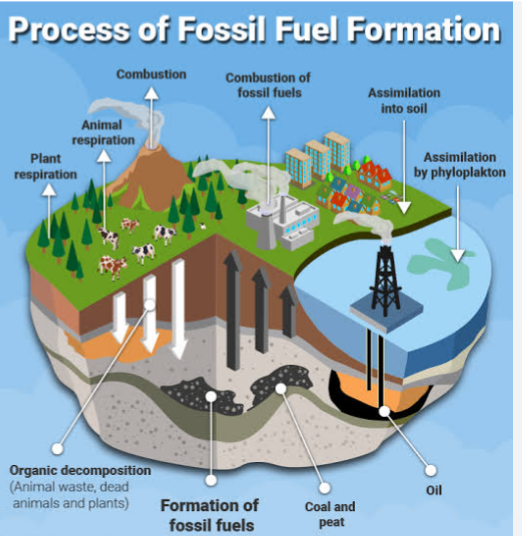
ENERGY FROM FOSSIL FUEL
The following terminologies must be well understood before explaining the energies from the fossil fuel.
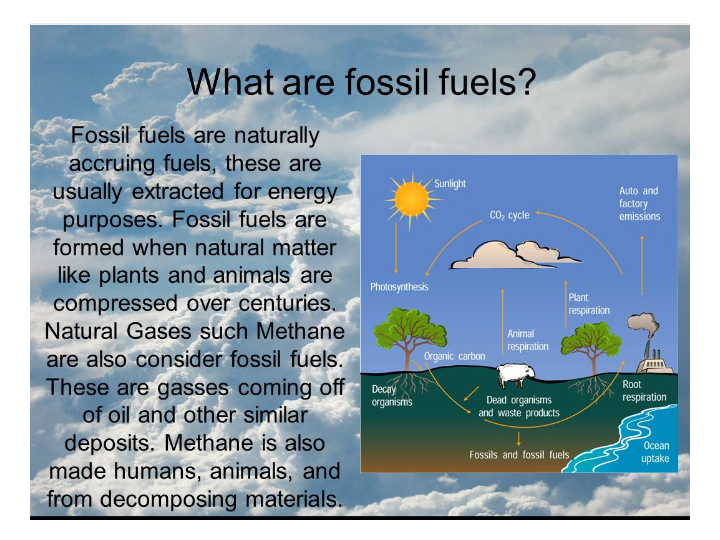
1. RESERVES: These are resources that are well known for geological exploration and are recoverable at current price and current technology
2. PROVEN RESERVES: These are reserves that are reasonably contain and being produced from reservoirs, under existing economy and technological conditions.
3. INDICATED RESERVES: These are unproven reserves that are believed to be recoverable from some known experimental fields using some known geological, geo-physical, geochemical explanation techniques.
4. INFERRED RESERVES: These are those reserves that are inferred from demonstrated reserves-petroleum. It’s a mixture of hydrocarbon. That is, oxygen, hydrogen and carbon with an average ratio of 1:7 of H2 and O2.

Petroleum pit originate from decay of organic matter usually materials that have being converted over million of years under high pressure and temperature usually associated with very deep bury. The petroleum that is formed under this condition can hydrate through the surrounding rocks and later accumulate in deposits from which it can be extracted. These deposited are usually found within reservoir rocks such as sand stone, shakes and lime stones which will normally hold the oil the way sponge hold water. These rocks are very porous and permeable allowing both liquids and gases to move. For the oil to accumulate, it is very essential that the reservoir rock is covered with impermeable rock that will act as a trap to prevent upward migration of oil and gas.
When an oil well is first drilled to a position of the content of the reservoir, the oil will be expelled from the sandstone due to natural pressure. A mechanical pump must then be used to bring the oil to the surface. To remove more oil from the ground, water is pond into the reservoir to cause the oil to come out. A technique called “enhanced petroleum recovery” is usually employed to recover bulk oil from the ground.
NATURAL GAS: it is a mixture of hydrocarbon primary methane by crude oil. It is naturally formed from decayed organic materials. Sometimes it may be mixed with oil and some other times it is usually trapped in regions where the oil is not very abundant.
Unlike crude oil, natural gas is not expensive. It is clean burning and it is readily available. It is a very good substitute for crude oil and has many uses, such as:
1. It can be used for space heating
2. Water heating
3. It can be used for fuel for boilers
4. As chemical feed stocks
5. To generate electricity
6. Production chemicals, fertilizers and hydrogen. etc.
COAL: America has abundant of coal in the world and it is always called Saudi Arabia coal. Coal is formed from plant materials in swampy areas millions of years ago. The vegetation will first decompose into pit as the land is subdivided. It will then be covered by mud and sand which form s limestone and sand stones. Both limestone and sandstone are usually formed on top of coal.

CLASSIFICATION OF COALS
Coals normally comes in four classification :
1. LIGNITES: These are youngest coal in terms of age formation. The geological pressure from the ground above and temperature have similarities to other land of coal and usually have high water content and low heating value.
2. SUB BITINUMUS COAL: These are formed under increased heat and pressure and with very high water content. These coal are of primary interest because of its low sulphur content. Two things are used to determine purity of coal :
a. Sulphur content
b. Cost of mining
These coal are found primarly in surface mines of the great plain.
3. BITUMINUS COAL: These are formed under conditions of pressures and heat. They are the most abundant types of coal. The heating value is very high and also it’s sulphur content which is usually about 2% of weight of coal.
4. ANTHRACITE: This is a very hard coal with high healing value. It burns longer than other type of coal but it is limited in supply, that is, it is not abundant in supply.
FUEL FROM ROCKS
Millions of years ago, nature usually traps decaying vegetation in sedimentary rocks, some deposite of which are so rich is called oil shale. Oil shale is an organic compound also refer to as kerogine that can actually be burn. When rocks are crushed and heated under normal conditions, 15 – 30 gallons of oil shale per tonnes are produced.
PROCESS OF EXTRACTING OIL SHALE
Process of extracting oil shale is simple, that is, the shale is mined, crushed and then heated to 300 degrees. Sometimes reaching 450 degrees under a process called” oil restoration”. This is quit very easy because there are no high pressure or capability process involved. Apart from oil shale, another important source of crude oil is called tar sand. These are similar to oil shale in that their oil cannot be recovered by convection Al drilling process.
Tar sand contains the highest viscous oil like that of asphalt and it is normally called bitumen.. To recover these oil, sands are extracted by the process of mining and then they are mixed with hot water to extract the bitumen. The largest deposite of tar sands in the world is found in Canada. In summary, fossil fuel continues to be the greatest challenge even to the next century.
Natural oil and gas can accumulate within the rocks beneath the surface of the earth especially in reservoir rocks. Exploration of oil and gas is usually done by seiomic method. That is, some particular type of waves called the selsmic wave are produced by explosion of the surface, reflection from the explosive is measured by a seismometer.
Coals are formed from plant materials and are usually classified based on their carbon content. Bituminus coal has a high heating value and it is the most abundant in supply. The demand for coal will be determined by environmental conditions such as sulphur IV oxide and carbon dioxide. Coal can be converted to oil and natural gas by the process of ” liquifractional gasification”.
RADIATION
Radiation is present everywhere, from sunlight to microwave to nuclear radiation. It is almost impossible to avoid exposure to radiation as human being. Radiation comes in many forms as both waves and particles and can have beneficial and harmful effects on living things. The most important types of radiation are : Gamma rays, X rays, and charged particles such as electrons and alpha particles.
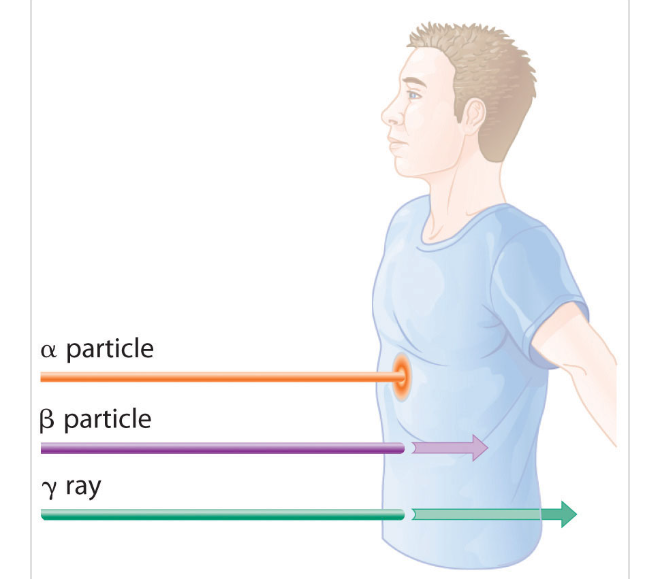
Gamma rays and X rays are not charged and so they cannot ionize alone directly through electrical interaction. However they produce electrons indirectly through other interactions with matter.
To be able to quantify radiation, units are set or used. Radiation are measured in ” rads” . The rad therefore is defined as the quality of radiation that delivers 100ergs of energy to 1g of tissue. The rad is a short form or acronym r-radiation, a – absorbtion, d-dose.
The dose of radiation can also be measured in another unit called rens.
Rens can be defined to be numerically equal to the Adsorption dose in rads much like by a particular quantity called quality factor.

Radiation dose in rens= Adsorption dose in rads multiply by Qf.
Qf is therefore defined as the ratio of rens to rads and it is also called ” relative biological effectiveness” such as :
gamma ray have Qf=1 and
neutron and Proton has Qf=5.
Alpha particles have high energy neutron and high energy proton of Qf higher than 20
EFFECT OF EXPOSURE OF HUMAN BODY TO RADIATION
Radiation interact with human cells primarily by causing chemical reactions of water molecules in the body and some other substances like DNA and protein molecules.
The effect of high radiation dose may appear within hours or days. It can cause ordinary vomiting, or lead to death. It can also cause cancer, genetic damage, mutation which may be passed to generation unborn.
The following are rate of effects of exposure of radiation on human body:
1. One rads of dose radiation essentially cause no detection change.
2. 10 rads makes the blood to change chemically
3. 100 rads destroys some catal tissues causing skin colouration changes
4. 200 rads causes injuries and physical disabilities
5. 2000 rads result in instantaneous death.