Crop production operations are associated with land preparation which involves the use of crude tools or farm machines at various stages of the cultivation. In general, there are two forms of land preparation.
1. Primary tillage operation
2. Secondary tillage operation
PRIMARY TILLAGE OPERATIONS
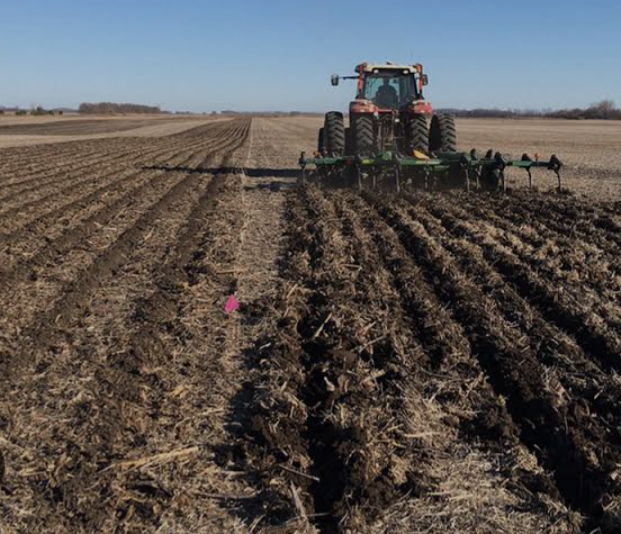
Primary tillage operation which involves ploughing of the field is done to loosen the soil, and destroy vegetation on the field. Plough drawn by animal or tractor is used for this tillage operation. Ploughing should be done on dry land and not on wet soil to prevent puddling or soil compaction. On sloppy land, ploughing should be done across the slope rather than down the slope to prevent runoff and erosion.

Ploughing facilitate planting and make the soil loose and friable for seed to germinate.
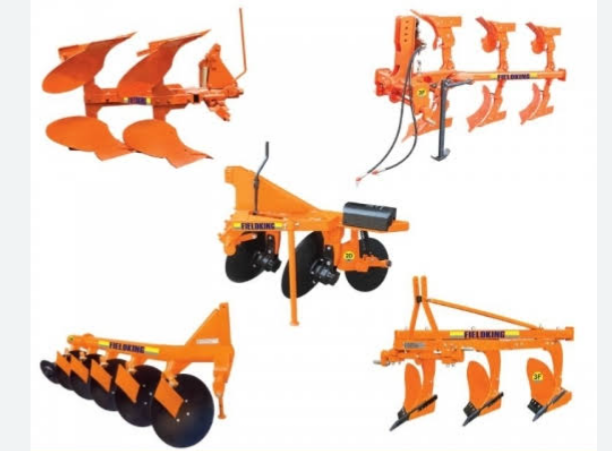
The plough is used for primary tillage operation. And there are different types of plough which include;
a. Mould board plough
b. Chisel plough
c. Disk plough
e. Sub surface plough
f. Rotary plough
B. SECONDARY TILLAGE OPERATION
Secondary tillage operations are tillage operations that convert land that had undergone primary tillage to a smoother seedbed or flat surface prior planting. It tends to produce a smoother soil surface. The main objective of secondary tillage is to prepare a seedbed or flat field into a fine crumps structure after primary tillage. Some of these operations include harrowing, ridging or mounding, inter tillage operation, etc. This tillage operation is carried out prior to planting. Some of the machines used include harrow, ridger, rollers, pulverizers etc.
PRIMARY TILLAGE EQUIPMENTS
THE PLOUGH: plough is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. The working of the plough is controlled by hydraulic system of the tractor.
PARTS OF PLOUGH :
1) Plough Bottom
2) Plough Frame
3) Attachments (Coulters & Jointers)
4) Wheels
5) Lifting Mechanism
6) Plough Hitch
7) Depth Adjusting Mechanism
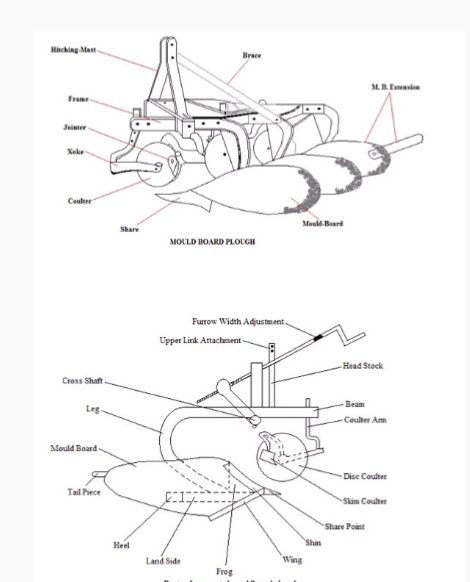
1) PLOUGH BOTTOM : It is the main part of the plough and it has three side wedge. It is made up of three main parts i.e. mould board, landslide and share which are rigidly fastened to the frog. Its main function is to cut the furrow slice, shatter the soil and invert the furrow slice to cover trash. The size of the plough bottom is the width of furrow it is designed to cut.
TYPES OF PLOUGH AND THEIR COMPONENTS
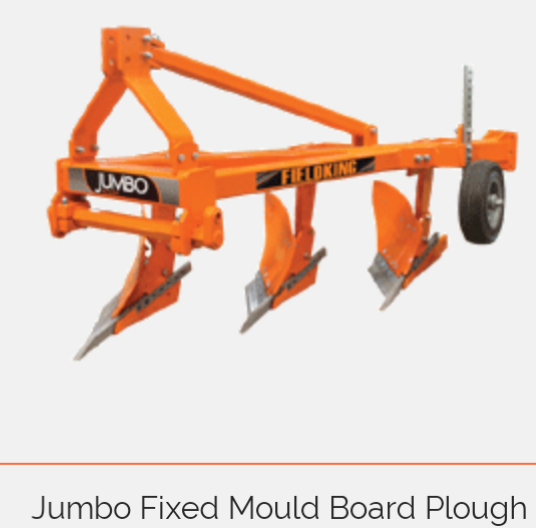
1. MOULD BOARD PLOUGH: Mould board plough is a primary tillage implement that is operated by a tractor and it consists of share point, share, mouldboard, landside, and frog, shank, frame and hitch system. It turns the soil in furrow slice and turn the vegetation on the land into the soil. It also breaks the soil into clods and lumps, thus, creating a rough soil surface. Other importance of mould board plough are: It cuts trash and buries it completely. It is also used for turning green manure crop which decay and turn to humus in the soil. It is also used for turning and mixing compost, farmyard manure or lime into the soil.

TYPES OF MOULD BOARD PLOUGHS:
There are three types of mould board ploughs. They include:
1. Trailing MB plough
2. Semi mounted MB plough
3. Mounted MB Plough
1) TRAILED MB PLOUGH: It is also known as pull type and it is complete unit hitched by the drawbar of the tractor and supported on two wheels. It has1-8 bottoms depending upon the capacity of the tractor. Single bottom has one bottom. Two – Eight bottoms are called as gang mould board.
2) SEMI-MOUNTED MB PLOUGH: These are more compact and more maneuverable than pull type. They have thesame Sizes and number of bottoms as that of the pull type. They are less expensive but put more vertical load on tractor rear wheels (there by improving tractive ability).

3) MOUNTED MB PLOUGH : They are also called direct mounted, tractor mounted or tractor carried ploughs. They can be lifted by the tractor lift linkages which are controlled by hydraulic system of the tractor. It is available in 2-5 bottoms depending upon the capacity of tractor. The number of mounted ploughs can cause instability of the tractor during transport.
CLASSIFICATION OF MOULD BOARD PLOUGHS 1) ONE WAY PLOUGH : The plough has a single set of bottom which turns the soil to the right hand side.
2) TWO WAY PLOUGH : It turns soil to both right and left side. The plough has two sets of bottoms mounted on a common frame that is rotated about a longitudinal axis to change from one set to other using mechanical or hydraulic cylinders for the rotation. And uses gage wheels and rear wheels which are automatically repositioned as the plough bottom frame rolls over. Some set of bottoms have their own wheel (For example, mounted ploughs).
The two way ploughs eliminate the back furrow and dead furrow leaving the field more leveled for irrigation or drainage. Two way ploughs are advantageous for terraced fields or contour ploughing and for small irregular shape fields.
Animal drawn two way plough is called a turn- wrest plough.
a. MOULDBOARD: Mouldboard is that part of the plough which receives the furrow slice from the share. The mould board is specially designed for different purposes. It lifts, turns and breaks the furrow slice. It is made up of hardened shaped alloy of steel. This gives reason why it has different shapes and sizes. The mouldboard is of following types: a) General purpose b) Stubble type c) Sod or Breaker type and d) Slat type.
b. THE SHARES: Share is the part of plough bottom which actually penetrates into the soil and makes a horizontal cut below the surface. It is mounted at the front end of the mound board. It is responsible for cutting of the soil into furrow slice. As it is continously used, it is subject to wear and should be removed and replaced.
PARTS OF THE SHARE
i. SHARE POINT : It is the forward end of the cutting edge which penetrates into the soil .
ii. CUTTING EDGE : It is the front edge of the share which makes horizontal cut in the soil.
iii. WING OF SHARE : It is the outer end of the cutting edge of the share. It supports the plough bottom .
iv. GUNNEL : It is the vertical face of the share which slides along the furrow wall. It takes the side thrust of the soil and supports the plough bottom against the furrow wall.
v. CLEAVAGE EDGE : It is the edge of the share which forms joint between mould board and share on the frog.
vi. WING BEARING : It is the level portion of the wing of the share, providing a bearing for the outer corner of the plough bottom
The different types of shares are : Slip share, Slip nose share, Shin share and Bar point share.
c. THE CUTTER: The cutter function in making a partial vertical cut of furrow slice so that the mould board breaks the furrow slice neatly
d. THE SHARE POINT : The share point is of bar type and is made from high carbon steel or low alloy steel.
e. LAND SIDE :Land side is the flat plate which presses against the furrow wall, resisting the side pressure exerted by the furrow slice on the mould board and prevents the plough from lateral swinging. Thus, stabilizing the plough while in operation.
The rear part of land side is called heel which slides on the bottom of the furrow. Land side is fastened to the frog with the help of plough bolts.
f. FROG : Frog is the part of the plough bottom to which other components like share, land side and mouldboard are attached
It is an irregular piece of metal. It may be made of cast iron for cast iron plough or it may be welded steel for steel ploughs.
g. TAIL PIECE : Tail piece is an adjustable extension, which can be fastened to the rear of the mould board to help in turning the furrow slice.

2. DISC PLOUGH: The disc plough consists of common main frame, disc beam assemblies, rockshaft category-1 or category-2, a heave spring loaded furrow wheel and a gauge wheel. It is made up of a large circular disk with each disk having a mould board share and a cutter. The disk is about 750 to 900mm in diameter with its angle ranges from 40 to 450 to obtain the desired width of cut. The plough also have a tilt angle which determines the width of the ploughing. The tilt angle is the angle between the plane of the disk and the vertical or direction of travel. As the disk rolls over the soil, it cuts and turn the furrow slice. Some model disc plough is designed to operate as 2, 3 or 4 bottoms, by adding or removing sub beams. The sub beam are assembled according to requirement.
This disk plough is suitable for tropical soils that is dry and hard or rough stony or peaty soil where the mould board will not turn the slice. It is advantageous than the mould board plough because it makes a deep ploughing.
3. ROTARY CULTIVATOR: The rotary plough has an L shaped blades which cuts up and pulverised the soil by a rotary action of the cutting knife. The cultivators does not totally bury the trashes in the soil and will chop up long vegetative materials. They are mostly used to chop plant residues. There are different types of rotary plough. They inclide: tractor mounted rotary plough, pulled Auxillary rotary plough and self propelled garden rotary plough
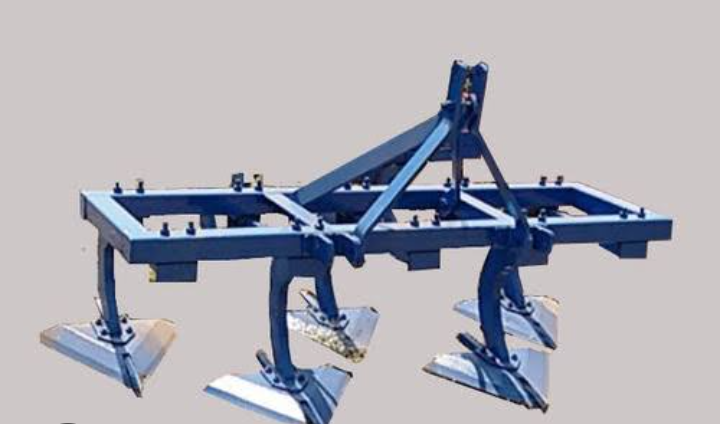
4. TYNE CULTIVATOR OR CHESIL PLOUGH : Cultivators are mechanical implement for breaking up the ground and uprooting weeds. Cultivator consists of a frame, tynes (fixed or spring loaded) having reversible shovels and 3-pont hitch system. Cultivators are primarily used for intercultural operation after the crop has come up a few centimetres above the ground. But cultivator is also used for opening the land, preparing the seed bed and sowing of the seeds. Cultivators for the secondary tillage are available as animal drawn and tractor drawn especially in medium and light soil. Duck foot type cultivators are used for primary tillage operation
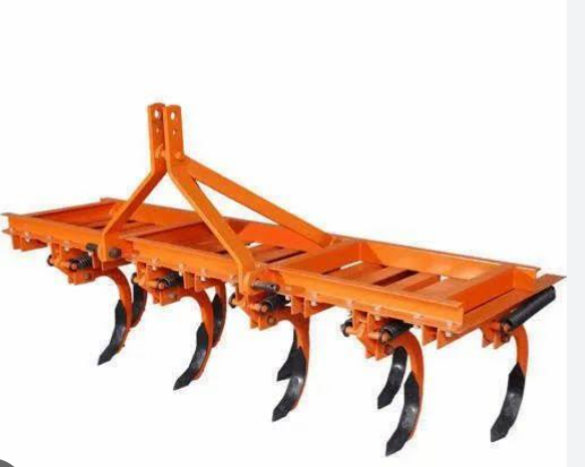

5. DUCKFOOT CULTIVATOR
The duckfoot cultivator consists of a box type steel rectangular frame, rigid tines and sweeps. The sweeps are triangular in shape similar to foot of duck, hence called duckfoot cultivator. The sweeps are made from old leaf spring steel and fixed to tines with fasteners, which makes them replaceable after being worn out or becoming dull. The tines are made of mild steel flat and forged to shape. It is a tractor-mounted implement and depth of operation is controlled by hydraulic system. The sweep cultivator is popular in black cotton soils. This cultivator is mostly used in hard soils for shallow ploughing.

SECONDARY TILLAGE EQUIPMENTS
1. HARROW: These are used to level the soil and crush clods and destroy weeds.
TYPES OF HARROW
a. Disk harrow
b. Spike tooth harrow
c. Spring tooth Harrow
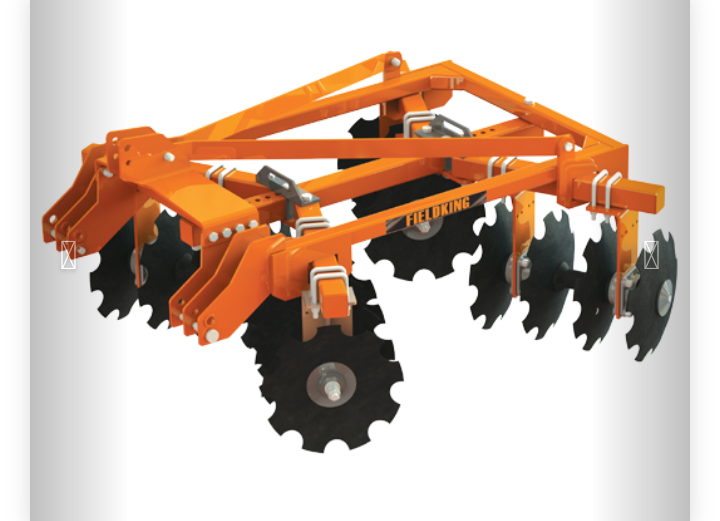
a. DISC HARROW
The tractor mounted disc harrow consists of two gangs of discs mounted one behind the other. The disc on front gang throws soil outwards and the rear gang inward. Therefore, no soil remains uncut by the offset disc harrow. Disc harrow is secondary tillage implement. It is used after the primary tillage. It is used to break the clods developed during primary tillage operation.

3. RIDGERS: Horticultural crops require loosened soil. Therefore, ridges are required for such crops. Ridgers are used for making ridges. And there are different types of riders. They include:
a. Mould board disc ridger
b. Rotary ridger

4. HOEING AND INTER- ROW CULTIVATORS
There are three types of hoeing equipment. They are used to destroy weeds along the inter rows of the growing crops. They include: fixed blade, rotary blade and ground driven rolling cultivators. They distroy weeds between crop rows and also allow limited recultivation and incorporation of chemicals.

