
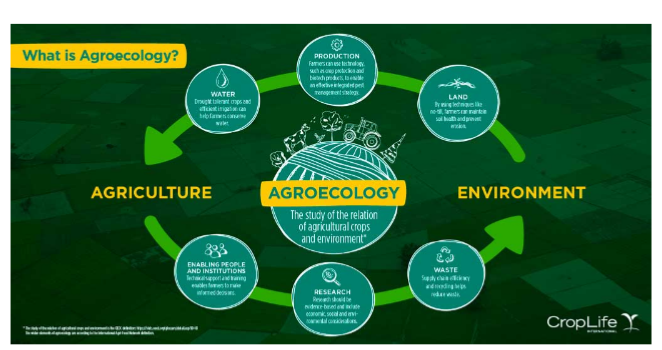
Agroecology is the bed rock of sustainable agriculture. It is a combination of agro and ecology to form the word Agroecology. Agro means agriculture and ecology means relationship among living organisms and their surrounding environment. It is the practice and science of applying ecological concepts, knowledge, and principles to the design and management of sustainable farms. It proffer solutions to environmental and economic pressures that are faced by agriculture of today. And it aims at promoting sustainable food systems, respectful of people and the environment.
Agroecology manifest as a scientific discipline, agricultural practice, or political or social movement.
AS A SCIENCE – Agroecology studies relationships between organisms (that is plants, animals and microbs) in different agricultural systems. It also focuses on environmental impact at farm scale. Some people also describe it as entire food system or the ecology of the food system. Others describe it as the application of ecological concepts and principles to the design and management of sustainable food systems .
AS A SET OF AGRICULTURAL PRACTICE : An agroecological practice is one that is not environmentally harmful. Agroecology is seen as a new, modified and adapted practices that contribute to more environmentally friendly, ecological and organic or alternative agriculture. It is used to improve traditional and indigenous agriculture in developing countries. For instance, in traditional agriculture, practices emback on are mainly for soil fertility, organic matter management, resource conservation, or techniques for low external inputs system. Therefore, agroecology is aimed at productive, sustainability, and resilience farming systems using minimal synthetic, nontoxic external inputs. This is achieved by employing other farming practices apart from using agrochemicals to optimize processes and interactions in agro-ecosystems. For example, Crop rotation, polyculture, agroforestry, use of manures and compost etc. It seeks for ways to improve agricultural systems through the utilisation of natural processes, creating beneficial biological interactions and synergies amongst the components of agro-ecosystems. In many places, Agroecology incorporate off farming practices, employ ecological processes and ecosystem services for the development and implementation of agricultural practices
AS A MOVEMENT : An agroecological movement may be a farmer group working for food security, sovereignty or autonomy or it may be a political movement of the local population for rural development. This movement are action driven which are set towards a common goal of sustainable development and sustainable agriculture.
Agroecology is seen as a solution to modern environmental challenges such as climate change and malnutrition. It aims to transform social and political and economic structures affecting farmers and his production systems so as to advance food sovereignty and social justice.
Agroecology is similar to many techniques used by small scale farm holders by minimising cost and building on traditional farming systems. It gradually expanded to farmer- to- farmer teaching and collaboration with rural social movement on a global scale
Agroecology offers various environmental benefits compared to industrial farming. It offers less pollution, less dependent on fossil fuels, less damage to soil and natural resources and more agricultural biodiversity which improves resilient of farming system.
BENEFITS OF AGROECOLOGY
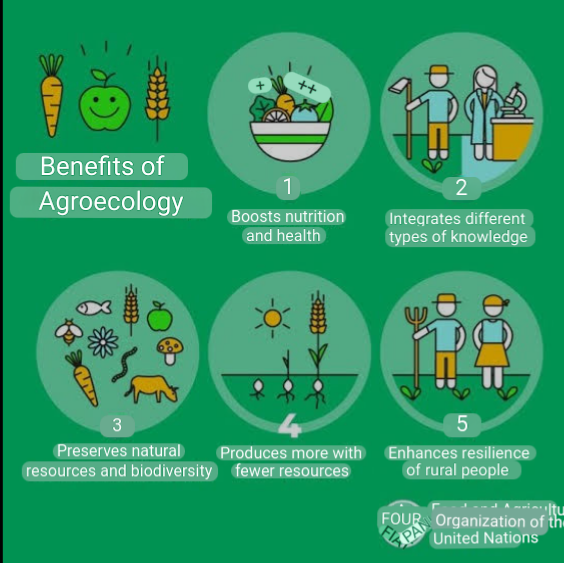
1. Agroecology integration all the components on the farm and diversify the rural available to the entire families,
2. It increase opportunities for women to participate.
3. Agroecology are characterized by greater biological and human resilience crucial to face climate change.
4. It brings about great level of productivity and sustainability
5. It utilize fewer chemicals like fertilizers and pesticides.
6. Less fewer water is utilized for farming
7. Agroecological approach increases ecological resilience, health and nutrition, biodiversity and natural resource conservation, and produces a much more economically stable environment.
8. It help to mitigate the effects of climate change by reducing dependency on fossil fuels and fuel-based agricultural products.
9. Agroecology makes farms more resilient to various natural disasters, climate change impacts, and the stresses created by economic and environmental systems.
10. Many small-scale farms vulnerable to damages from natural disasters have adopted agroecological methods to withstand the more adverse effects.
AGROECOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES
Some of the agroecological principles include: recycling; input reduction; soil health; animal health; biodiversity; synergy; economic diversification; co-creation of knowledge; social values and diets; fairness; connectivity; land and natural resource governance; participation etc. Some of these principles are briefly discussed below:
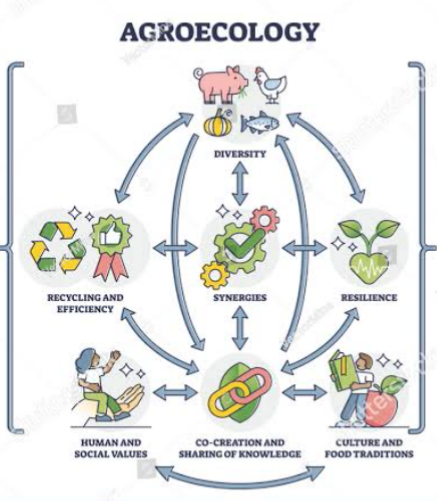
1. PARTICIPATION :Agroecology encourage and promote the active participation of farmers and other agricultural stakeholders in decisions about various farming practices. Through this, the local economy becomes strengthened , farmers are empowered, and culture well preserved. The merging of both traditional and modern knowledge result in high agricultural productivity and sustainability and environmental preservation.
2. SOCIAL EQUITY : The agroecological approach seeks to promote social equity, value the participation and involvement of rural communities, ensure fair access to land and natural resources, strengthen family farming, ensure means of production for family farmers and rural communities and promote social justice in countries.
3. LAND AND RESOURCES GOVERNANCE : One of the main focus of agroecology is the protection of family farmers and sustainable managers who seek to preserve natural resources like lands. It seeks to provide equitable access to land and natural resources which are incentives for the long-term investments that are necessary to protect soil, biodiversity and ecosystem services.
4. SOIL HEALTH : Healthy soil is vital for optimization of food production and plant growth. For soil to be healthy, there is need for maintenance of the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soil, and this is possible through the adoption of different agronomic approaches. The diversification of nutrient sources from chemical source to organic sources, adoption of principles of conservation agriculture, enhancement of soil microbial diversity, efficient resource recycling through the integrated farming system, and amendment addition for correcting soil reactions are options required for improving soil health,
5. CO-CREATION OF KNOWLEDGE : As it is being said that two heads are better than one applies to this principle. Agroecology encourages stakeholders in agricultural sectors including rural farmers to participate and share knowledge regarding farming tactics or scientific discoveries for the collective benefit of all.
6. SOCIAL VALUES AND DIETS : Agroecology also focuses on creating food systems that suits each region’s traditions, culture, identity, social and gender equity and societal norms through provision of healthy, diversified, seasonally and culturally appropriate diets.
7. PROMOTE BIODIVERSITY : Agroecology contributes to the Cultivation of different varieties of crops and integrating them with different agricultural enterprise such as livestock. This help to preserve biodiversity, improve sustainable food production and create a balance in the ecosystems.
8. SYNERGIES: Achieving synergies among agricultural components is an agroecology design principle that provides multiple benefits to food production systems. Synergies are enhanced when crops, animals, and aquaculture are integrated in a mutually beneficial ways. For example, integration of crops with livestock can help improve soil fertility and health without reliance on synthetic fertilizers to increase soil fertility. Integration of crops with aquaculture, agroforestry and tree growing can provide ecologically sound solutions for soil erosion, pest control, and nutrient cycling.
9. NUTRIENT RECYCLING : Agroecology relys on the utilisation of natural resources to enrich or improve the nutrient status of the soil. Instead of using external chemicals fertilizers, livestock manure and plant residues are used or recycled to produce nutrient rich material called compost, farmyard manures and other methods that enrich the soil in a more natural way.
10. ADOPTION AND INTEGRATION OF BOTH MODERN AND TRADITIONAL KNOWLEDGE : Agroecology combines both traditional knowledge of local communities with mordern knowledge of agricultural practices to create a sustainable agricultural practices that will supply the needs of the populace. It place values on traditional knowledge.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN AGROECOLOGY AND SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE
Agroecology is an approach that promote sustainable food production and environmental preservation. Both Sustainable agriculture” and ecological agriculture” are two terms used synonymous. People use them interchangeably but the two concept differ from one another and they create a lot of confusion based on their usage.
Both agricultural practices are environmentally friendly and socially responsible, but with different approaches to overall agricultural production.
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE : Sustainable agriculture is a broad approach to farming that aims to meet the needs of existing and future generations, while also ensuring profitability, environmental health and social and economic equity.
The primary focus of sustainable agriculture is on maintaining the long-term health and productivity of the agricultural ecosystem. It involves techniques that emulate nature and promote soil health, prevent water pollution, protect biodiversity, minimize the use of synthetic inputs such as pesticides and fertilizers, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Some common practices of sustainable agriculture include: crop rotation, drip irrigation, Integrated Pest Management (IPM), mixed cropping and planting cover crops, etc. The goal of sustainable agriculture is to create a resilient and self-sustaining farming system that can adapt to changing environmental and economic conditions. It also aim at producing the greatest quantity of food over a long time in order to feed a growing human population while keeping the environment intact.
AGROECOLOGY : Also called ecological agriculture is a subset of sustainable agriculture that places a strong emphasis on ecosystem dynamics and mimicking natural processes in farming systems. Agroecology focuses on understanding and leveraging ecological principles to design agricultural systems that work in harmony with nature. It empower farmers, add value locally and give privilege to women to participate. It also allows farmers to adapt to climate change, sustainably use and conserve natural resources and biodiversity. It often involves techniques such as crop rotation, agroforestry, integrated pest management (IPM), no usage of chemical inputs but rely on naturally recycled nutrients and utilizing beneficial insects to control pests. The goal is to build greater resilience, efficiency and overall sustainability of the agroecosystem.
In summary, sustainable agriculture and agroecology aim to reduce the negative impact of agriculture on the environment while promoting resilience and productivity of the agricultural system.
