The negative impacts of climate change on global food production, such as decreased agricultural output due to an increased frequency of floods and droughts has resulted in starvation and malnourishment at different places of the world.
Plants exposed to high levels of CO2 frequently show changes in the chemical composition of their leaves, stems, roots, fruits and tubers.
Increase in atmospheric CO2, Temperatures change and growing conditions change do affect the productivity of the soil. Even in “normal” conditions, there are plenty of places where the ground just isn’t conducive for farming. For example desert region and concreted floors.
Nowadays vegetables are being imported by different countries. They are shipped in from afar, and before they gets to their destination, they would have lost nutritional value along the way. This calls for the development of a new technology that will solve the soil challenges encountered during crop production so that every soil of the world can be productive . Thus, the initiation of hydroponics.

Hydroponics is a method of culture formed from two Greek words hydro meaning “water,” and ponos, meaning “labour”. It is the technique of growing plants using a water-based nutrient solution rather than soil, and can include an aggregate substrate, or growing media, such as vermiculite, coconut coir, rock wool (molten rock that is spun into fibres), fused shale, clay pellets, rice husks, granite chips, sand, pumice and perlite.
It can be described as a way of not using the soil for planting but using other different material to support the roots of the plant, and grow crops directly in nutrient-rich water.
Fertilizer solution, often derived from animal or fish excrement or synthetic fertilizers, is pumped into the system periodically. The frequency and concentration of the fertilizer used depends on the plant requirement and on ambient conditions such as light and temperature. The system may be a recirculatory system or not where by the solution is drained into a tank, and pumped automatically. Periodic tests is carried out on the nutrient solution to know if their is still sufficient nutrients in the water, or there is the need for additional chemicals or water and also water pH .
TYPES OF CROPS GROWN IN HYDROPONICS FARMING
Hydroponics is used to cultivate ornamental crops, herbs, and wide variety of vegetables including cucumbers, lettuce, peppers, and florist can be grown satisfactorily with hydroponic systems. Other crops include spinach, kale, fodder, tomatoes, and radishes etc,
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF HYDROPONICS FARMING
Hydroponic systems have a number of advantages and disadvantages compared with cultivation in soil.
ADVANTAGES OF HYDROPONICS FARMING
1. SAVES LABOUR: Hydroponics save labour. Automatic watering and fertilisation is carried out with little human effort.
2. EVERYWHERE FARMING: Hydroponics allows growers to produce food anywhere in the world, at any time of the year, and to get higher yields with fewer resources. This system of farming can be set up indoors in places that would not normally be available for the growing of plants, such as in urban areas where the population is dense, at desert areas, behind restaurants, on concreted floors, in the atmosphere and have even been studied as a potential method of crop production aboard spacecraft.
3. CLIMATIC FACTORS : Climate is not a factor in hydroponics. Hydroponic systems use less water compared with conventional way of growing plants. In indoor hydroponics system, the environment are controlled. Artificial lighting is usually carried out except if greenhouse is used. Water is also supplied in a recirculatory system to make the farming easy. Nutrients are supplied through the water system compared to conventional system where the soil supplies plant nutrients and rain or irrigation system supplies the water need.
4. COMPETITION : Competition for space, nutrients, sunlight, air and water are hindering factors to crop production in conventional farming. In hydroponics system, the plants produce less root and their is low nutrient competition. Sunlight, air, spacing and water are taken care of and higher yield is realised. Individual plants can be planted close together as sufficient nutrients are in solution to go round all plants. When nutrient level is low, addition is done.
5. LESS RISK OF PEST AND DISEASES :Pest and diseases are problems faced in Conventional farming. They cause about 70% of crop loses all over the world. In hydroponics system, proper care and management are practiced to ensure higher yield. High preventive measures are put in place and peradventure any infestation of pest occurs, quick control measures are carried out before all plants become affected. Organic pesticides are utilized for pest control. Synthetic pesticides are not used because it can pollute the water used for the farming. To cap it up, there is no soil-borne diseases and less risk of pest infestation especially in indoor hydroponics farming.
6. SIZE OF FARMING : Hydroponic farming can be practiced on a small- as well as large-scales settings. People who do not have a large space, such as restaurants, eateries, those that live in apartments or those that do not have a garden, and those living in highly densed urban area can successfully use hydroponics to grow plants.
7. SUSTAINABILITY: Hydroponics farming provides a sustainable food cultivation practices. There are some plants that cannot be supported in a hydroponic setting. These include deep rooted crops, like potatoes, yam, cocoa, tree plants that grow tall, and vines etc. The farming type supports more vegetables crops which are good sources of vitamins and minerals, flower production and fodder for ruminants. It also helps growers produce nutrient-rich plants much faster without the use of pesticides.
8. HIGH YIELDING VENTURE : In a hydroponic farming, pesticides are not used because there is less risk of pest infestation especially in indoor type. No reliance on seasons before production. In addition, plants get the required nutrients directly in a solution, and adequate management is practiced. These makes the crops to develop faster and free from pest and diseases that lower yield. Therefore, crops can be grown all year round, without having to lose crops to external factors like pest infestation, weather changes, and disease outbreak.
9. RECIRCULATORY WATER SYSTEM RESULTING IN REDUCED WATER CONSUMPTION :
Hydroponic farming is a good farming technique in areas with water shortage. Little water is used in the farming compared to conventional agriculture. The water solution is reused and recirculated through the pipes in the setting. When unused water leaves the planting channels, the water is sent to the nutrient solution reservoir where it is analysed and nutrients are added again to meet the plant needs. The water is then sent back for the plant usage.
10. TIME SAVING SYSTEM: Traditional farming requires a lot of effort and time from soil analysis to tillage to weeding, watering, fertilisation and harvesting etc. All these are time consuming.
In contrast, hydroponics farming only requires little time to set it up in preferred space and grow the plant. All necessary operations that might delay production are encompassed in a simple system. No weeding, mulching, irrigation or waiting for season before planting and lots more.
DISADVANTAGES OF HYDROPONICS FARMING
The disadvantages of hydroponics farming include:
1. HIGH INSTALLATION COST: The cost of installation of hydroponics equipment is high such as water pump, reservoir, air pump, water treatment plant, and electrical cables etc. 2. HIGH SET UP COST: large-scale system of hydroponics require a high investment. There is need for proper planning, system designing and budgeting. The system is highly automated and modern technologies are used to set it up. Technologies required for initial installation includes: air pump, water treatment plant, nutrient tank, lighting, reservoir, temperature controller, etc. Electrical and plumbing systems may require a huge initial budget.
3. WATER ANALYSIS: There is need to test the solution on a frequent bases. Water pH and toxicity from excess nutrients along side algae growth can affect hydroponics farming. Plants uptake nutrients from the solution and there is need for continuous nutrients supply till the plant reaches harvestable stage. Compared to planting in the soil, some nutrients still hang up in the soil for plant usage.
4. SYSTEM ERROR: Any small errors in the system can affect the whole crop and lead to total collapse of the system. For example, non functioning of the air pump to produce oxygen can drown the plants. Also, if the water lacks the necessary nutrients required for growth, the plants would die. Therefore, adequate monitoring of the system is required.
5. REQUIRES SPECIAL EXPERTISE : Hydroponic systems are very vulnerable to equipment failure or power outage, which can kill the plants within a few hours. The equipment and techniques involved in the system need someone with proper knowledge and expertise on how to operate them. The plants will likely not grow without the appropriate expertise, which can affect the yield negatively causing heavy loss. etc
FOUNDATIONAL ELEMENTS OF ANY HYDROPONIC SYSTEM.
These are the key variables required for a successful hydroponics farming.
1. Fresh water: Most plants prefer water with a pH level around 6–6.5.
2. Oxygen: In traditional farming, at night, oxygen is used up for respiration by the plants. Roots of plant take in the oxygen from soil micro pores. In hydroponics systems, depending on the setup type, spaces can be created between the base of the plants and the water reservoir, or the containers be oxygenated like those in fish tank. Air stone can be bought and laid on the base of the containers or air pump installed to the water container.
3. Root Support. In conventional farming, soil is the growth, water and nutrient medium. and also provide anchorage to the plant roots. In hydroponic system, materials like vermiculite, perlite, peat moss, coconut fiber, and rock wool etc are used for root support. While nutrient solution provide the nutrients needed by the plants. Materials that compact like sand or gravel that don’t retain any moisture should not be used.
4. NUTRIENTS : Both micro and macro nutrients are required for plant growth and development. In hydroponics system, plants require sufficient amount of these nutrients to stay healthy and productive just like plants grown on soil that requires nutrient for healthy growth. Such nutrients can be supplied from fertilizers. These plant nutrients are dissolved or mixed with the water to form a nutrient solution before feeding it to the plants.
5. LIGHT . For indoors hydroponics farming, lighting sources are needed. Therefore, lighting source should be purchased and installed. The Daily Light Integral (DLI) which is the amount of light required by the different plants is supplied by providing a light regulator installed with the light source to regulate the amount of light needed by the different plant species.
COMPONENTS OF A HYDROPONIC SYSTEM. 1. Growing media: Growing media is the substitute for soil. They are inert media that support the plant’s weight and anchor the plant roots but do not provide any nutrient to the plant. They are porous and retains moisture and nutrients from the nutrient solution which it then delivers to the plant.
2. Air stones and air pumps : Plants roots submerged in water can quickly drown if the water is not sufficiently aerated. Air stones disperse tiny bubbles of dissolved oxygen in nutrient solution reservoir. These bubbles also help distribute the dissolved nutrients evenly in the solution. Air stones need to be attached to an external air pump through opaque food grade plastic tubing (the opacity will prevent algae growth from setting in) to generate oxygen as found in aquarium.
3. Net pots : Net pots mesh like materials used to hold hydroponic plants. The material allows roots to grow out of the sides and bottom of the pot, giving greater exposure to oxygen and nutrients.

TYPES OF HYDROPONIC SYSTEMS
Two systems of growing plants in hydroponic settings are:
ACTIVE SYSTEM
The active system is a very complicated system whereby the roots of the plants have direct access to nutrients in water solution. Water pumps are used for circulating nutrient solution from a reservoir to the roots of the plants. After the plants absorb the nutrients, the excess solution not absorbed is sent back into the reservoir and nutrients are added again for circulation

PASSIVE SYSTEM
A passive system does not require a pump to circulate the solution. Instead, the plants are suspended in the solution. Different methods such as gravity, flooding, or capillary systems are used to move the water upwards to reach the suspended roots. This is the easiest type of hydroponic system that can be installed for usage.
The water should be changed Occationally because the water is stagnant and will result
in algae built up which would degrade the water quality.

TYPES OF HYDROPONICS FARMING SYSTEMS
1. NUTRIENT FILM TECHNIQUE (NFT)
Nutrient film techniques uses active system whereby the nutrient solution is pumped into a slopy channels where plant’s roots dangle and the shoot held upwards. The nutrient solution flows down the slopy channels, over the roots and back into the hydroponic reservoir. NFT hydroponic systems do not use grow medium but uses foam net pot to secure the plant.

Due to the size of the channels, NFT hydroponic systems work best for plants that have small root system, like leafy greens. It is also a simple system that can be easily set up, use to grow a lot of plants, which makes it a system recommendable for commercial growers. It easly scales to a variety of different applications, thus, it’s wide application property and usage in commercial farming and home growers.
Scalable means it can be alter to allow for the growth of a large number of plants at the same time.
2. DEEP WATER CULTURE (DWC)
The DWC hydroponic systems uses passive method whereby the plant’s roots are suspended in the nutrient solution and air is provided directly to the roots with an air stone or diffuser. The plants are placed in net pots and grow medium like coco coir, vermiculite, or perlite are used to anchor the roots.
Deep water culture works great for almost all plants but works especially well for large plants with big root systems or ones that grow an abundance of fruit. Examples of DWC is hydroponic bucket also called a bubble bucket and plastic totes. Plants grow and develop faster in this farming system.

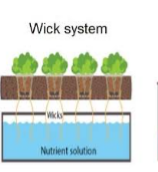
3. WICK HYDROPONICS
The wick system is a complete passive system. It is the simplest type of hydroponic system that require no electricity, pumps, or aerators.
The plants are placed in an absorbent grow medium like coco coir, vermiculite, or perlite to anchor the roots and a nylon “wick” is run from the plants into a reservoir of nutrient solution.
Due to the facts that wick hydroponic systems only supply little nutrient solution to the plants, the systems can only work well for small HOUSE plants and herbs. Plants that don’t require much water grow well in wick systems such as small garden plants and herbs. Heavy-feeding plants cannot be grown with this system as they demand for more nutrients the wick system cannot provide.
4. FLOW OR FLOOD AND DRAIN SYSTEM
Ebb and flow hydroponic systems (also called flood and drain) is an active system whereby plants are placed in large grow beds filled with grow medium. Water pump is used to flood the grow bed with nutrient solution until it reaches a certain point just below the top of the grow medium. A drain is used to maintain the level of the water below the top of the medium so as not to overflow. The water pump is controlled by a timer. After running for a predetermined amount of time, the timer shuts off the pump which allows the water to run back down through the pump, draining the grow bed completely.
Also, an automatic drain can be used instead of using timer pump. Automatic drains flooding and draining mechanism is quicker and more frequent.
The major disadvantage of the ebb and flow system is that the pump controller can malfunction. And when this happens, all operations are halted until the pump is fixed or replaced.
Ebb and flow hydroponic systems is best for all vegetables especially root vegetables .
As the plants take in nutrient solution and the water level drops, the roots grow deeper into the reservoir keeping a section of the roots submerged

.5. THE KRATKY METHOD OF HYDROPONICS
The kratky method of hydroponics is the only passive hydroponic method that does not require any electricity nor water or air pumps.
A reservoir is filled with nutrient solution and the plant’s roots dangle on top of it without making contact. An air gap is created between the top of the water and the roots. This gap provides air to the roots to breathe. Without the air gap, the plant will drown
6. DRIP SYSTEMS
This is an active hydroponic system that can be quickly altered for different types of plants. The nutrient solution is pumped into a tube that sends the solution straight to the plant base. At the end of each tube is a drip emitter that controls how much solution is placed into the plant. The flow of the solutions can be adjusted to met the needs of each individual plant.
They can be a circulating or non-circulating systems. In the circulating system, there is continuous drip of the solution. Extra nutrients in solution are sent back into the tank that holds the nutrient solution. The limitations of these circulating system is the need to consistently maintain the fluctuating nutrient and pH levels of the solution to recirculate the solution.The main advantage is that the system can be used to grow any plant.

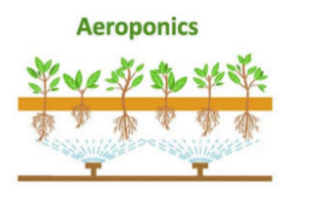
7. AEROPONICS SYSTEM
Aeroponic systems are difficult to build. In this system, mist nozzles are connected directly to the water pump. Nutrients solution is sprayed through the nozzles to the roots of each plants suspended in air. The mist nozzles are positioned below the plants. During the spraying, excess solutions will drop down and be collected into a reservoir positioned below the roots.
Plants in aeroponic system are suspended in air. From the air, they get all the oxygen that they need. This system also uses less water than any other hydroponic system.
Nearly all types of plants can be grown in an aeroponic system depending on the depth of the reservoir. Large plants need deep reservoir. Some of the limitations of this system are: they can be costly to build. The nozzles that spray the nutrients might also become clogged from time to time, which can be frustrating to clean.