
Technology advancement in the agricultural sector had broken the ground of hard labour in tilling the ground to easy practices of soiless farming. Preparing the soil for planting, working in the ground and plant to plant application of fertilizers are tidious farm work which has brought about great limitations in the farming practices . Lots of young graduates and unemployed youths now see Agriculture as a no go area due to hard-work and not a quick money earning venture. But today, growing high-value crops in water and soil-free media, a practice called HYDROPONICS , has brought a twilight into the Agricultural sector of the world.
Hydroponics is the growing of crops in a soiless medium. The soiless media may includes growing plants either on inert growing media (or substrate) or in an aqueous medium with bare roots. These media provide plant support, nutrients solution and retain moisture for plant uptake. To optimize this system, fish farming is now introduced into hydroponics system, an integrated system called AQUAPONICS. Aqua means water and phonics means to work or grow.
According to FAO (Food And Agriculture Organization), Aquaponics is the cultivation of plants and aquatic animals in a recirculating environment.
Aquaponics System can also be defined as the integration of Aquaculture and Hydroponics systems together to form a single farming system.
AQUACULTURE is the production of seafood for commercial purposes. FAO also describes aquaculture as the captive rearing and production of fish and other aquatic animal and plant species under controlled conditions. The aquatic species cultured include fish, crustaceans, molluscs, aquatic plants and algae.
In aquaculture, toxic nutrients accumulates from the fish food left over, the fish and the fish wastes meaning the water must be constantly syphoned off for a change with clean water or else the fishes will die.
There are two main types of aquaculture—marine and freshwater. And there are four major categories of aquaculture which include: open water systems (e.g.cages, longlines), pond culture, flow-through raceways, and recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS).
Aquaponic systems can be practiced in subsistence (or small scale) or in small indoor to large commercial units. It uses either freshwater, salt water or brackish water systems.
In aquaponics system, bacterias are used to convert fish waste to plant nutrition. This is an environmentally friendly, natural food-growing method with attributes of aquaculture and hydroponics merged together. There is no need of discard water or filtrate or add chemical fertilizers but recycled and reused in the system.
HOW AQUAPONICS IS DESIGNED
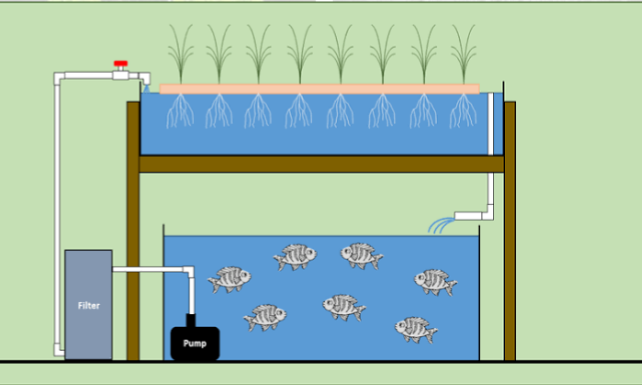
1. Aquaponics depends on an important nutrient process called the Nitrogen cycle. Fishes produce ammonia (NH3) which are acted upon by nitrifying bacteria called nitrosomonas. These bacterias appear on the wet surface of the aquaponics system at night. The AMMONIA (NH3+) is converted to nitrites (NO2-). Nitrobacter then convert the nitrite to Nitrate (NO3+). The nitrate is a nutrient absorbable by the plants
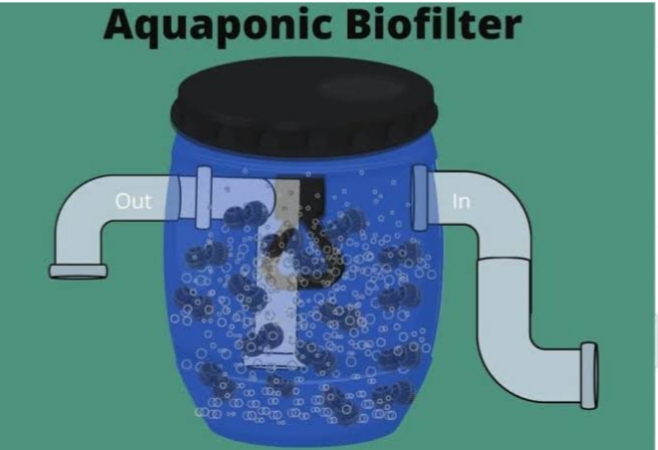
2. BIOFILTER: The biofilter is made from inorganic substances like gravel or hydroponic substrates. They provide an area for the beneficial bacteria to live and proliferate. The biofilter provides the dark wet surfaces for which the nitrosomonas act on the ammonia and the nitrobacter act on the nitrite. Water from the fish tank is pumped through the biofilter for the two organisms to convert the nitrite to nitrate. The water is then pumped to the crop tanks where the plant absorb the nitrate. The water becomes purified by the plants and the water pumped back to the fish tank again.
3. Fish eat the food given to them to produce excreta waste. The excreta waste (urine and fecal matter) are both rich in ammonia, which is toxic to the plants and fishes. The ammonia together with un-eaten food and decaying plant matter are converted by beneficial bacteria to organic nutrients that the plants can use. As plants uptake the nutrients, they also help in purifying the water for the fish usage.
In summary, aquaponics systems rely on 3 main components or enterprises: aquatic animals (the fish), nitrifying bacterias, and plants. All the three living components depend on each other for survival.
BENEFITS OF AQUAPONICS
1. BETTER AND RELIABLE FARMING PRACTICES: In aquaponics , both the challenges of hydroponic and aquaculture are mutually resolved to create a better farming system of aquaponics
2. DUAL OUTPUTS: Both aquatic organism like fish, crabs, shrimps and crop produce are outputs from the system. These output can be a source of food for the family or source of income to the farmers.
3. SUSTAINABLE FOOD PRODUCTION : Aquaponics is an intensive food production system that is sustainable. Continuous production of crops through out the year and fish produce and products can be achieved. Over- harvesting of fish in the wild is brought to a limit and endangered species and extinction of fish species is limited. Also, resources from one enterprise is used for the survival of the other. Therefore, aquaponics is a sustainable production system
4. INTEGRATED FARMING : Aquaponics encompasses hydroponics and aquaculture. Two components, fish farming and crop production are sources of produce realisable some the single system of aquaponics.
5. WATER PURIFICATION AND RECYCLING: Aquaponics is an extremely water-efficient system. The water used by fishes to survive is purified by the plants as they uptake the nutrients produced from fish waste. No need of draining the water as found in some aquaculture system. And also sourcing for irrigation water as in traditional agriculture is not done in aquaponics . The water are recycled and reused.
6. SOILESS FARMING: Aquaponics does not require soil and therefore it’s not susceptible to soil-borne diseases. Growing medium used include aqueous solution and substrates.
7. NON AGROCHEMICAL VENTURES: Aquaponics does not require the usage of fertilizers or chemical pesticides. Organic materials can be used. Organically treated seeds are used as agrochemicals are detrimental to the survival of the aquatic organisms.
8. ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY : Due to the fact that no agrochemicals are used and let out of the aquaponics system, a safe environment is produced. Recirculation system of the water produces healthy aquatic organisms and crops.
9. HIGH LEVEL BIOSECURITY : Due to the fact that a high level of care and management of the components of aquaponics are maintained, a higher level of biosecurity and lower risks from outer contaminants is incurred in the system
10. LOW LEVEL OF COMPONENT LOSSES: The losses from traditional farming may be due to pest and diseases attack, losses during harvesting, poor soil fertility, poor weather conditions and overpopulation etc. Aquaponics allows a higher control on the components and their environment than in traditional farming. Factors causing losses are taking care of.
11. NO RISTRICTION TO GENDER AND AGE: Aquaponics is not labour effective and can be practiced by all genders and ages. It saves labour as most of the activities in which labourers are needed have being taken care of, such as weeding, mulching, tillage operations, Fertilizers Application, spraying pesticides etc. The major operations in aquaponics are planting, feeding, harvesting, and monitoring of the system etc.
12. SOURCE OF NUTRIENTS : Aquaponics supply fish protein and other nutrients needed in diet by hydroponics crops. It also help in overcoming challenges of food insecurity. etc.
CHALLENGES OF AQUAPONICS
Among all odds, there are challenges in aquaponics. Such challenges or limitations include:
1. COST EFFECTIVE : The initial start-up costs of aquaponics is high compare to traditional farming, hydroponics and aquaculture. Facility installation, equipment needed, technical knowledge and lots more, add up to increase the set up cost. 2. KNOWLEDGE OF EXPERTS AND MANAGEMENT REQUIRED: Aquaponics requires deep expertes from different professions to be successful. The farmers need to have knowledge not only on growing crops alone but also on fish farming, and how fish and bacteria work. And technical skills regarding plumbing or wiring are also needed
3. EASE OF SYSTEM FAILURE: A little mistake in the management of the system can easily cause its collapse compared with stand-alone aquaculture or hydroponics. Any mistake in the two systems can easily be remediated and proffer solutions to. But in aquaponics where integration of the two systems are used, extra care and management must be introduced.
4. HIGH ENERGY USAGE: The energy demand in aquaponics is high and costly. Energy is needed to recycle the water system on a 24hours/7 days. Also, the indoor aquaponics require energy to power the light source, operate the biofilter, pump the water and control the temperature within the enclosed building.
5. EFFECTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT: Majority of the failures in aquaponics systems is due to ineffective waste management. An aquaponics system needs an effective break down and filteration of organic wastes such as fecal matter and urine from the fishes which is done by the bacterias or algae in the system. A biofilter where the process will take place before the nutrient become available to plants are needed.
MATERIALS NEEDED TO SET UP AQUAPONIC SYSTEM
1. FISH TANK :. It can be made from plantic or aluminium. The size of the tank will determine the stocking density of the fishes.
2. MEDIA BEDS TO GROW PLANTS :. The media bed can be gravel or hydroponics substrates.
3. FLOATING TRAYS :. Rough beds will be needed for floating trays if used for planting.

4. BIOFILTER :. Media beds serve thesame purpose as biofilter.

5. WATER PUMPS :. Used to circulate water through out the system.
6. ENERGY SOURCE: To connect the systems, electricity would be needed.
7. WATER HEATERS OR COOLERS :. This is used in temperate regions. It is used to heat the water during winter and cool the water during summer.
SPECIES OF FISHES TO RAISE IN AQUAPONICS
The species of fishes to raise in aquaponics in different regions depend on the climatic conditions of that region, likewise the crops to plant. In tropical regions, stocking cool water fishes might not be able to cool the water when the water becomes warm.
Regular testing of the water pH and Dissolved oxygen level should be carried out on regular bases. It can be done on weekly bases to ensure habitability of the water environment.
The fishes include

1. EDIBLE FISHES : tilapia, catfish, silver perch, jade perch, Murray cod, barramundi, trout, bluegill,
2. ORNAMENTAL FISHES : goldfish, koi, siamese fighting fish betta, guppies, white cloud mountain minnow,

Some ffactors to consider in choosing fish species for aquaponics include fish types, tank size, feeds, climatic conditions of the region, compatibility of different fishes and fish sizes.
FISH FOODS : sinking and floating pelletized feeds, spinach, bloodworm, flaky feeds, small crustaceans like crabs, shrimps, veges (not all), worms, Insects of different kinds, plankton, etc.
TYPES OF AQUAPONICS SYSTEMS DESIGNS The types of aquaponics systems designs include
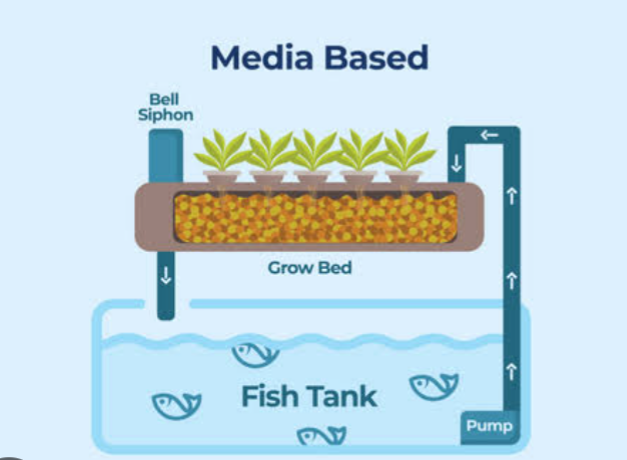
1. Media Based,
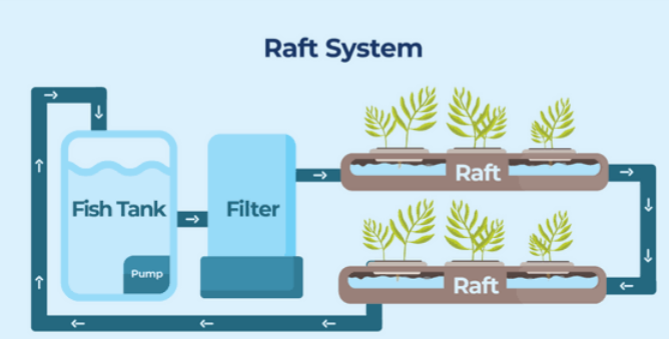
2. Raft System,
3. Nutrient Film Technique.

4. Vertical Aquaponics System

5. Hybrid System.

