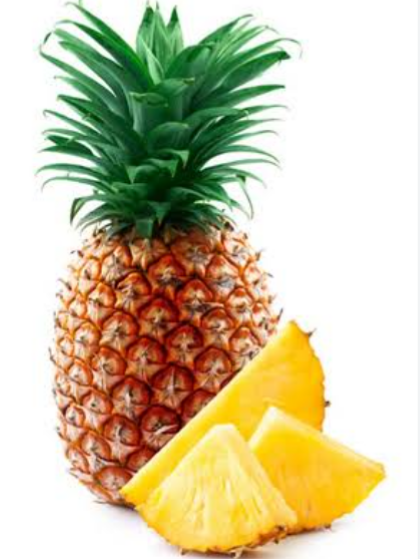
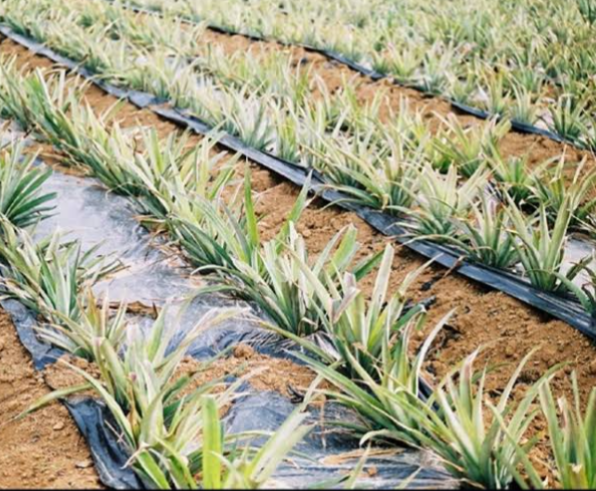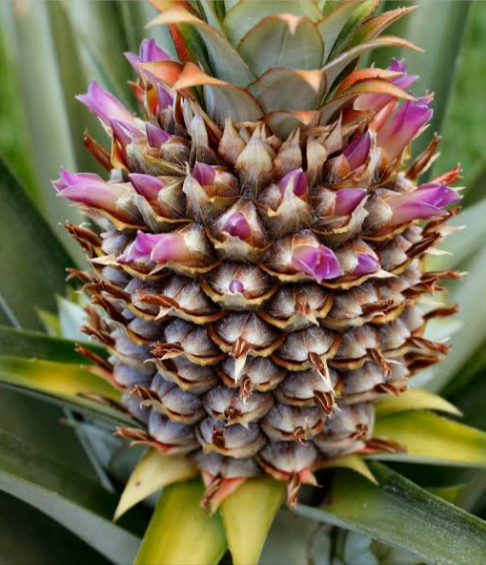
Pineapple (Ananas comosus) is the most favorite fruits of human. It is known for its rich, sweet taste, flavour and spiny texture. It belongs to the family Bromeliaceae, order Bromeliales, geneous Ananas and species comosus.

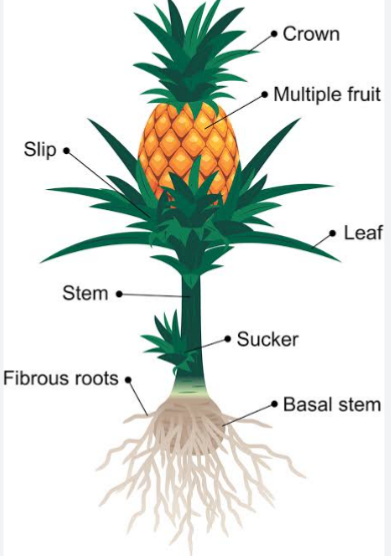
Pineapple is a short lived perrenial monocot with a short main axis. It is an herbaceous plant that grows up to a height of 1.5 meter. The pineapple is a multiple fruit, meaning it is formed from a cluster of flowers (called an inflorescence) growing on a catkin. The leaves are dark green on the upper side and whitish on the lower side. There are between 30 to 40 stiff succulent leaves closely spaced in a rosette on the thick fleshy stem. The fruit is fleshy, trough – like and grooved with sharp spines along the margins. The fruit can be eaten fresh or processed into canned juice to be taken.
There are about 30 cultivars of Ananas comosus cultivated in the tropics and subtropical regions of the world. For conveniences in the global trade, all the cultivars are grouped under five main classes. Only two cultivars of are cultivated in Nigeria. The smooth Cayenne which has smooth leaves and the rough Cayenne. Other cultivars include Red Spanish, Queen or rough cayenne, Perolera and Pernambuco.
The fruit is covered by the floral bracts. In the middle of the fruit is a swollen stalk of inflorescence which serves in conducting water and nutrients to the leaves. The fleshy carpel is yellowish in colour.
VARIETIES OF PINEAPPLE
Varieties of Ananas comosus found in other parts of the tropics include: A. ananassoides, A nanus, A bracteatus, A friztmuelleri, A lucidus, A parguazensis, A macrodontes
Seed production of Ananas spp is rear because most of these varieties possess reduced fertility combined with self incompatibility.
BENEFITS OF PINEAPPLE
1. The fruit is a good source of minerals like Magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, zinc and calcium, vitamins like vitamin C, and vitamin B1.
2. It is used as ingredients in pizza, condiments, cake, sweets, pastries, yogurts, ice creams, drinks, flavouring agents etc

3. Pineapple contain a proteolytic enzyme called bromelain. The enzyme is used for meat tenderising agent and medicinal purposes.
4. The enzyme is discovered to interfere with the growth of malignant cells, inhibiting platelets aggregation, fibrinolytic and anti inflammatory action.
5. The enzyme is also known in enhancing drug absorption and removing skin (debridment)
6. Pineapple leaves juice are used as purgative ( agents that cleans the bowel)
7. The leaf juice are also used as emmenagogue ( agents that induce menstrual bleeding) and vermifuge( agent that expel intestinal worms)
8. The stem and leaves are good source of fibre which can be processed into paper.
9. Pineapple fibre can also be processed into fabric materials. Cloth made from such fibre are called pina cloth.
10. Parts of pineapple plants are converted into hay and silage fed to cattles
11. Juice from pineapple can be converted to alcoholic beverages.
12. Eating pineapple helps to reduce the risk of cancer, ease digestion and boost the immune system.
13. Raw pineapple can be used to make jam, jelly, and folk medicine
14. Pineapple is traditionally used in the Philippines as an antihelminthic agent to expel parasitic worms (helminths) from the body
15. Pineapples are low in calories and high in fiber, making them an alternative for people who wants to lose weight
FACTORS THAT AFFECT THE CULTIVATION OF PINEAPPLE
Factors like temperature, rainfall, altitude, soil requirement, location, drainage and soil nutrient status all influence the production and development of pineapple plant. Having knowledge about this factors helps in taking care of the soil on which the pineapples are planted and hence increase production.
1. CLIMATIC FACTORS AND TEMPERATURE: Pineapples thrive best in hot and humid tropical and subtropical climate.
a) TEMPERATURE :The most preferred temperature for pineapple cultivation ranges between 18 to 44oC.
b) ALTITUDE :Altitudes do affect pineapple production. It determines the flavour of the fruits. Acid concentration of the fruits increases with increase in altitude. While decrease in altitude result in decrease in fruit acidity level
c) RAINFALL: Optimum rainfall required for cultivating pineapple is between 1400 to 1500 mm/annum. Planting pineapple in cold regions is not adviceable.
2.FIELD PREPARATION : The soil should be ploughed, harrowed to level the ground. All soil cluds, debris and rocks should be removed. After leveling the ground, make trenches of about 90 cm wide and between 15 to 30 depth.
3. SOIL REQUIREMENT : A well drained sandy loamy soil that is rich in organic matter is required. The pH of the soil should range between 4.5 to 6.5. This favours good growth of the fruit crop.
Heavy clay soil that is waterlogged can harm the crop. To use such soil, the soil should be well drained
3. PLANTING: The planting season depend on the peak of flowering. The planting season is from December to March. Planting can start from April to June or from August to November. Planting should not be done during heavy rainfall.
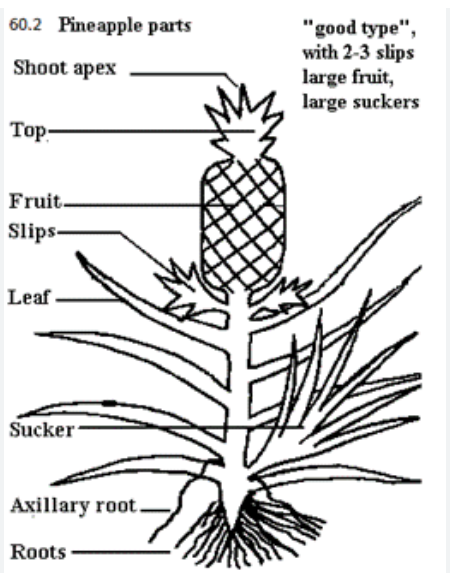
4. PROPAGATION: Pineapples are perennial crop. They are propagated using vegetative propagules which include suckers, crown, hapas or slips.

The propagules can store without the parent plant for 6 months. The propagules should be treated with fungicides and insecticides before planting. Planting materials will start flowering after 12 months of planting. For crawn, flowering starts between 19 to 20 months after planting. And fruiting starts between 19 to 20 months in the tropics.
5. PLANTING METHODS: The planting methods depend on the soil, rainfall and planting materials. Crown propagules are sensitive to deep planting. While slips and suckers are planted to a depth og 10 to 15 cm
a) SPACING: For commercial purposes, high density population is recommended. A planting density of 63,400 plants/hec can be obtained at a spacing of 22.5cm* 60cm*75cm at subtropical regions. That is 22.5cm from plant to plant within the line and 60cm from plants within the line (in between two lined) and 75cm between two double lines. While at hot humid tropics, planting density of 53, 300 plants/hec can be realised at the spacing of 25cm*60cm*90 cm. That is 25cm from plant to plant within the line and 60cm from plants within the line (in between two lined) and 90cm between two double lines
b) FERTILISER REQUIREMENTS : Nitrogen fertilizer is required for leaf production. N:P:K 16:12:12 can be applied. 40 to 50 tonnes of farm yard manure can be applied. Nitrogen fertilizer is applied in split dose. First application is done 2 months after planting and second dose is applied 12 months after planting. Phosphorus and potassium. Are also applied in split dose. First dose at planting and second dose applied 6 Months after planting.
6. IRRIGATION: During rainy periods, irrigation is not needed in pineapple field. Supplementary irrigation can be used during dry spell. This will help increase the fruit size.
7. INTERCULTURAL PRACTICES: These are other operations carried out on pineapple field. They include mulching, weeding, earthen up, removal of splits and leaflets, pest and disease control and harvesting.
a) MULCHING: Dry leafs, and plastic mulch can be used for mulching. Mulching helps to conserve water in the soil and make it available for the pineapple plant. It also help to control Weeds along and in between the rows
When fruits are matured, they can be covered with polythene nylon to protect fruits from sun burn and bird attack.

b) EARTHEN UP: Earth along the interspace rows can be collected and placed at the surrounding of the root zone. This helps the plant which is shallow rooted to anchor properly to the soil
c) REMOVAL OF SLIPS AND LEAFLETS: During plant development stage, slips will be produced on the plant. Slips should be removed to prevent delay in fruit maturity. Leaflets should also be reduced at 45 days after fruit sets. This increases fruit quantity and size.
d) HARVESTING: 5 months after planting, plant begin to produce flowers. Fruits begin to emerge 12 to 16 months after planting.
Pineapple are highly perishable fruits. Fruit colour is an indicator of fruit maturity and ripening. Fruits can be harvested when their is slight change at the fruit base (for organic harvesting). But for table purposes, fruits can be harvested when the fruit changes colour from green to golden yellow. Other fruit quality indices include firmness, size, absence of decay, sunburn, cracks, bruises, brown spots, gummosis and Insect damage
e) PEST AND DISEASES : Pests like mealybug, scale insects, spider mites, nematodes, fruit borers and sap beetles can damage pineapple.
Diseases such as stem rot, butt rot, mealybug wilt, fusariosis, fruit let core rot and internal browning can be caused by excessive irrigation or waterlogging conditions etc. To avoid this, proper soil drainage and exposure to sun should be carried out. Also, treated planting materials should be used for propagation.

IMPORTANCE OF PINEAPPLE FARMING
1. EMPLOYMENT OPPORTUNITIES : Pineapple farming creates job opportunities for people, thereby reducing unemployment rates in countries. People get jobs as farmers, farm worker, workers in canneries that process pineapple into other products, sales of pineapple and propagules etc
2. Income Generation: farmers who plant pineapple for commercial purposes realise good money from the sale of the produce. Traders earn money from the sales of pineapple fruits and propagules. Also, through exportation of pineapples and their products, countries realises high revenue.
3. Food Security: Countries who engages in pineapple production do provides fruits for local consumption and reduces the importation of foreign pineapples. These pineapples provide a great health benefits in the life of the populace. Refer to importance of pineapple above
4. Foreign Investment: It attracts foreign investors who invest in pineapple farming in the country, thereby creating more job opportunities.
5. Sustainable Agriculture: Pineapple farming is a sustainable agricultural practice that ensures the continuous production of pineapple fruits for local consumption and exportation.



