
A mushroom (Agaricus spp) or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus. It belongs to the kingdom Fungi, phylum Basidiomycota or Agaricomycetes, family Agaricaceae, order Agaricales and classified into different genera such as Agaricus, Pleurotus, and Lentinula etc . It is typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. Mushroom is referred to as the edible sporophore while Toadstool is referred to as the inedible or poisonous sporophore.
Structurally, mushroom has an umbrella-shaped fruiting body called sporophore with thin, bladelike gills on the undersurface of the cap called pileus where the spores are shed and a fleshy stalk called stipe and roots or underground network of threadlike strands called mycelium. The mycelia can survive from a few months to many years before they die depending on the available food substrate. As long as nourishment is available and temperature and moisture are suitable, a mycelium will produce a new crop of sporophores each year during its fruiting season.
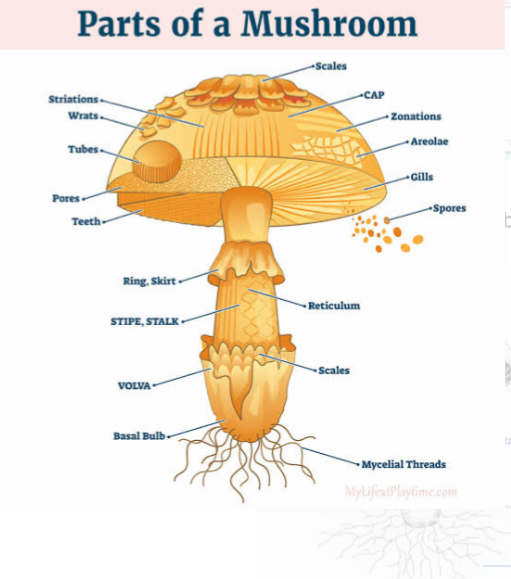
IMPORTANCE OF MUSHROOM
1. FREE OF CHOLESTEROL : Mushroom have no cholesterol in it. It contain small amounts of essential amino acids, minerals and vitamins.They contain many minerals, like selenium, potassium, copper, iron and phosphorus, that are not often found in edible plant foods. Mushrooms are rich in B vitamins: riboflavin (B2) , folate (B9) , thiamine (B1) , pantothenic acid (B5) and niacin (B3) .
2. IMPRESSIVE NUTRITIONAL PROFILE (VALUES) : Mushrooms are special food delicacy with subtle flavour and agreeable texture. By fresh weight, the common commercially grown mushroom contain more than 90 percent water, less than 3 percent protein, less than 5 percent carbohydrate, less than 1 percent fat, and about 1 percent mineral salts and vitamins.
3 MUSHROOM POISONING: wild Mushrooms are Poisonous. When consumed, they cause mild gastrointestinal disturbance or slight allergic reaction. It is important that every mushroom intended for eating be accurately identified
4. EFFECT ON AGEING :. Mushrooms may help keep you young. Mushrooms contain a remarkable high concentration of two antioxidants, ergothioneine and glutathione. From researches, When these two antioxidants are present together, they work extra-hard to protect the body from the physiological stress that causes visible signs of aging (that is, wrinkles body).
5. MEMORY BOOSTER (BRAIN) AND OTHER BENEFITS: Mushrooms can protect your brain as you AGE. Mushroom is rich in polyphenols. Food containing polyphenols protect against cognitive decline in older adults. Other researchers have also proven that the antioxidants like ergothioneine and glutathione found in mushrooms do help prevent Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. They recommend eating at least five button mushrooms per day to reduce your risk of neurological illness in the future.
6.. The vitamin B(s) and copper in mushrooms assist in red blood cell development.
7. NO RISK OF HEART DISEASES: Unlike red meat and salts that possess a lot of heart problems. Meat contain fat that increases cholesterol level, mushrooms causes no heart diseases. It contain glutamate ribonucleotides that can replace salt. These reduceses blood pressure or heart disease risk. Mushrooms calori level is also low. Mushrooms also contain potassium, vitamin C, and fiber which also help in reducing cardiovascular health problems. Potassium can help regulate blood pressure, and reduce the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. But people with multiple diseases of heart and kidney disease may need to consume less potassium because potassium complicate kidney problems, so doctors advices are needed.
8. DEVELOPMENT OF HEALTHY BONES: Mushrooms can assist in strengthening your bones. From research findings, Mushrooms grown outside in UV light are good source of vitamin D. Such mushrooms convert the ergosterol in them directly into vitamin D. This vitamin D in the mushrooms can meet the daily vitamin D requirement in human, keeping the bone healthy.
9. REDUCES THE RISK OF CANCER : Mushrooms are a good source of ergothioneine, an amino acid and antioxidant that prevents or slows cellular damage. Therefore, incorporating varieties of edible mushrooms into daily diet will reduce the different types of cancer in the body. Such cancers include prostate, colorectal, vaginal and breast cancer etc
Vitamin D and Choline ( an antioxidant) in mushrooms has also being proven in prevention or treatment of some kinds of cancer.
10. STIMULATE A HEALTHIER GUT
Mushrooms are forms of prebiotics, that stimulate beneficial bacterial growth in the gut.
Mushroom polysaccharides stimulate the growth of healthy bacteria when passing through the gut to the colon.
11. REDUCE RISK OF DIABETES : It is discovered from findings that people who eat a lot of fiber may have a lower risk of developing diabetes especially type 2 diabetes. For those who already have it, fiber may help reduce blood glucose levels. Raw mushroom is rich in dietary fiber called beta-glucans (70 grams (g) of which, provides 0.7 g fiber) which lower blood cholesterol levels. Beta-glucans are found in the cell walls of many types of mushrooms.
12. PREGNANCY : mushrooms is a good source of Folate required to boost fetal health.
MUSHROOM CULTIVATION

Mushrooms can be grown subsistently in home garden or in a big farm (commercial farms) . Mushroom farming involves the cultivation of mushroom (fungi) for consumption or medicinal purposes.
The mushrooms are grown on a suitable substrate under a specific controlled environmental conditions such as in a dark and humid space or outdoor . To start a mushroom farm, the farmer must put the following into consederation: Identification of the right species of mushrooms to grow, suitable growing conditions and appropriate marketing strategies.
BENEFITS OF MUSHROOM FARMING
1. SOURCE OF INCOME TO FARMERS: Few farmers engage in mushroom farming are making serious money especially in African countries like Nigeria and the process of starting mushroom farm is quite simple.
2. LOW START UP CAPITAL: Mushroom farming is not capital intensive even on commercial basis. The capital required to set it up is low and the return on it is high. The demand for edible mushrooms is quite high in the market. But in country like Nigeria, the demand is low compared to developed nations.
3. EVERYWHERE ENTERPRISE: Mushroom farming can be carried out in a small backyard garden, on large commercial farm, indoor, using vertical farms, etc.
4. EMPLOYMENT OPPORTUNITY : In countries like Nigeria, the high rate of unemployment among youths is a serious concern to the nation. Opportunities in mushroom farming can help solve the problems of unemployment. Apart from cultivating mushrooms, mushroom industry also provides employment. Such industries include: industries that package edible mushrooms; medicinal mushroom products producing industries; spawn-making companies, and wild mushrooms processing industries who process mushrooms into other products like compost.
Employment can also be in areas like developing seminars and training services, selling mushroom farming equipment, such as incubators, growing trays, and humidity control systems and mushroom exportation to other countries etc.
5. EASE OF SOURCING FOR MUSHROOM SUBSTRATE: Mushrooms can be cultivated all year round. Sources of mushroom substrate are readily available. Such substrates include food and Agricultural waste such as dry plantain leave, palm oil chaff, cassava peels, cotton waste paddy straw, cotton wastes, palm fiber, tree sawdust.
6. READILY AVAILABLE MARKETS: The main consumers of mushrooms are food restaurants, hotels, clubs, and households. Mushrooms are sold through vegetable shops, local markets, and superstores.
7. REDUCED ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION : Mushrooms cultivation is environmental friendly. It helps in reducing environmental pollution as large quantities of organic solid waste which ought to pollute the environment are used in its production.
SETBACKS IN MUSHROOM FARMING
Every farming enterprise has its own setbacks. In mushroom farming, some of the setbacks or challenges include:
1. ATTENTION : Mushroom farming requires a significant amount of attention to Detail. Temperature and humidity can affect the growth and performance of the fungi.
2. CHANGES IN ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS: , Any changes in the environmental conditions can affect the growth and quality of the mushrooms. 3. LABOUR INTENSIVE: Mushroom farming is labor-intensive, especially during the initial set-up and harvest periods.
4. CONTAMINATION: Improper sterilisation of growing medium can cause contamination or if the mushrooms are not handled correctly
STEPS BY STEPS MUSHROOM CULTIVATION PRACTICES
1. Selection of an edible mushroom species that will produce spores.
2. SELECTION OF SUBSTRATES: Substrate is the food medium for the growth of mushrooms and for the fungi to absorb nutrients. The substrates used include : food or agricultural wastes such as dry plantain leave, cassava peels, sawdust, and vegetable leaves contain lignin and cellulose
3. COMPOST ( GERMINATING MEDIUM) : Mushroom are usually grown on decomposed compost heap spread onto a long wooden boxes called beds. The compost is spread in the box and sawdust sprinkled on it to form the next layer. The layers are then watered, and mixed with food waste or agricultural waste (substrate) . The mixture is watered occationally until the sawdust decomposes with the food/agro waste thereby producing a very unpleasant odour. After five to six days, when the odour reduces, the farmer can then plant the mushroom spores (seeds) as soon as possible.
4. HEAT TREATMENT : This is a sterilisation process used to control pests (microorganisms) and diseases on the substrates. And also to get rid of soluble nutrients. Most substrates are given heat treatment before spawning. The heat treatment should be carried out immediately the substrates are sourced for before mixing with compost heap as stated above.
Three heat treatments methods can be used . They include:
Pasteurization by immersion in hot water
Pasteurization by steam
Sterilization
After substrate sterilisation, inoculation with mushroom spawn is then carried out.
5. SPAWNING : Mushrooms are cultivated using spawns( mycelia propagules ). The mushroom spawns are inoculated with the prepared compost. The Spawn is broadcasted on the compost and then thoroughly mixed into the compost using a handfork. A rapid growth of the Mycelia will occur. This will take place between 2-3 weeks.
Note: Spawns should be purchased in spawn-making companies, research institutes, or in the market. Spawns should not be sourced from the wild.
6. CASING : As the mycelium begins to germinate and grown all over the germinating media, casing should be carried out. Casing or casing layer is a layer of moist material that is put on top of the substrate with mycelium, before exposing this substrate to the fruiting conditions. The casing materials is made from compost and clay soil, without the food or agro waste materials added, making the mixture poor in nutrient compared to the germinating medium. This is carried out to initiate Fruiting. Without this step fruiting will not occur.
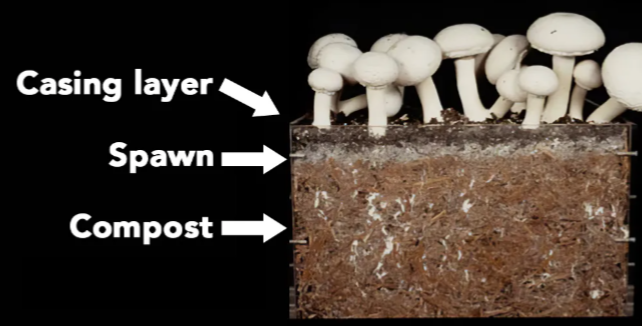
7. FRUITING AND HARVESTING : The period of fruiting may vary depending on the species, type of substrate used, and climatic condition of the growing room. Most Mushrooms reach maturity between 3-4 weeks after spawning. So harvesting can take place . It takes a week before new primordia are formed and about five to nine days for the second flush. Harvesting is performed by gently pulling or twisting or cutting at the base using knife to detach the mushrooms from the substrate. Generally, 3 or 4 flushes are taken over 4-6 weeks of picking and can be harvested over 2-3 months.
It’s important to harvest the mushrooms before they become too mature, as they will start to drop spores and lose flavor.
EQUIPMENTS AND MATERIALS NEEDED FOR MUSHROOM FARMING
1. SUBSTRATE : The common substrates include straw, sawdust, and coffee grounds.
2. PRESSURE COOKER OR STEAM STERILISER : They are used to sterilize the substrate or growing medium
3. MUSHROOM SPORES OR SPAWN : Needed for inoculation.
4. CONTAINER OR WOODEN BOX : needed to hold the substrate, and germinate the spawn. It can be a plastic bags, plastic trays or even wooden boxes. The container should be well paffurated inorder to allow for proper ventilation and drainage.
5. MIXING MATERIALS : Hand Fork or Hand Trowel and spade or shovel are needed to prepare the compost and mix thoroughly the substrate
6. GERMINATING OR GROW ROOM : which can be a small enclosed space in the home or a green house, or an enclosed building. In the grow room, the following should be installed: proper ventilation and lighting, temperature and humidity control systems
7. THERMOMETER AND HYGROMETER : for monitoring the temperature and humidity levels inside your grow room.
8. HARVESTING AND STORAGE MATERIALS: sharp knife or Scissors needed for harvesting and plastic bags or containers for storage etc
SOME MUSHROOM SPECIES

Some important edible and poisonous mushrooms species include:
Portobellos (Agaricus bisporus),
Shiitake (Lentinula edodes).
Honey mushroom (Armillaria mellea)
Dryad’s saddle (Polyporus squamosus), Beefsteak fungus (Fistulina hepatica),
Sulfur fungus ( Polyporus sulphureus),
Artist’s fungus (Ganoderma applanatum, or Fomes applanatus),
Cauliflower fungus (Sparassis crispa),
Milk thistle (Silybum marianum)
Horn-of-plenty mushroom (Craterellus cornucopioides).
Jelly fungi (Tremella species)
Ear fungus (Auricularia auriculara-judae).
Death cap, (Amanita phalloides)
common field mushrooms (Agaricus campestris) edible paddy straw mushrooms (Volvariella volvacea)
TERMINOLOGIES
* INOCULATION: Introduce of the fungal spore into a suitable substrate for growth.
*SPAWNING : means to generate or processes of releasing seeds to produce young especially in large numbers
*PROPAGULES : a vegetative structure that can become detached from a plant and give rise to a new plant, e.g. a bud, sucker, or spore
* SPORE : This is a reproductive cell that can develop into a new individual without uniting with another reproductive cell. Spores are distinguished from gametes, which are reproductive cells that must unite with gametes of the opposite sex in order to form a new organism.
* MYCELIUM : This is the vegetative part that grows to form the mushroom.
