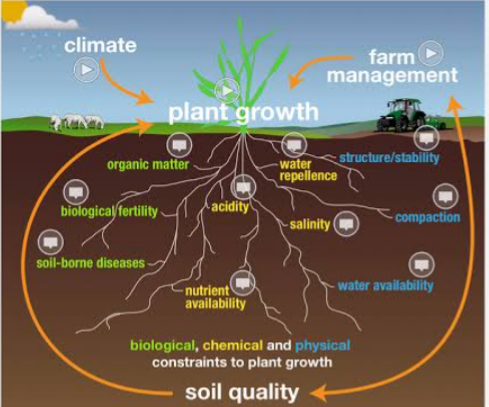
Soil quality can be defined as the fitness of a specific type of soil to function within its capacity and within natural or managed eco system boundaries, to sustain plant and animal productivity, maintain and enhance water and air quality and support human health and habitation. It also describe complex soil characteristics such as soil organic matter, nutrient amounts, and physical ( like soil structure) attribute , etc. These attributes are influenced by land management practices.
Soil quality is related to soil function. It determines the nutrients make up in foods stuffs produced by farmers to nourish human body needs. Quality soils are not only fertile but also possess beneficial physical and biological properties which gives clean air and water, increased crops harvest and forests, productive grazing lands, diverse wildlife, and beautiful landscapes. It is affected by soil properties such as soil texture, soil structure and cation exchange capacity (CEC).
Benefits of quality soils include : Good soil tilth with sufficient depth, sufficient but not excessive nutrient supply, small population of plant pathogens and insect pests, good soil drainage, large population of beneficial organisms no harmful chemicals or toxins that may harm the crop, and resilience to degradation and unfavorable conditions.
The only component of soil quality is soil fertility. Fertile soils are soils rich in plant nutrients which are in available form for plant growth and development. These nutrients are macronutrients and micronutrients. These nutrients are essentially needed by plants. In high-quality soil, the nutrients are available at rates high enough to supply plant needs, but low enough that excess nutrients are not leached into groundwater or present at high levels toxic to plants and microbes.
To determine if the soil on the field is high quality soil without laboratory analysis, The farmer should first know the properties of the soil. This would then lead him or her to how to improve on the soil quality that is degraded
FUNCTIONS OF SOIL QUALITY
1. Nutrient cycling
2. Water relations
3. Support plant growth
SOIL QUALITY INDICATORS, ASSESSMENT, AND THEIR MEASUREMENT
Soil quality is assessed based on the specific functions of the soil. The functions of the soil cannot be measured but the properties ( that is physical, chemical and biological) of the soil can be measured, which are used to quantify soil quality functions. Meaning that soil quality can be assessed by measuring soil attributes or properties that are referred to as soil indicators. These soil properties are called soil quality indicators.
Soil quality indicators are decision tools that effectively combine a variety of information for multi-objective decision making.
Soil quality indices selection is guided by the goal of ecosystem management. The goal of agroecosystem management differ by the interests and visions of different sections of people concerned with agriculture such as farmers, agronomist, horticulturist, botanist etc. Soil quality which is an aspect of environmental quality has an indirect relationship with agro ecosystem sustainability. When the management goals are identified, soil quality indexing can then be carried out.
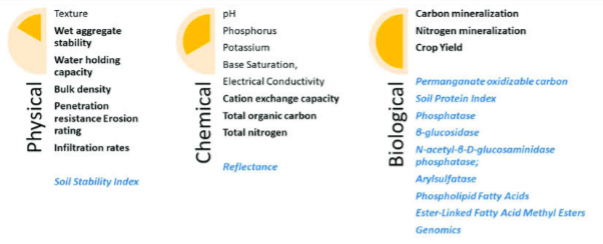
Soil quality indicators include physical, chemical, and biological soil properties that enhances soil functions. They include:
Soil pH, Avl. Phosphorus, Avl. Potassium, Total Nitrogen, soil Texture, O rganic Carbon, Exchangeable Cation, Cation Exchange Capacity,
Moisture Content, Bulk Density, Soil Organic Matter, Magnesium,Calcium and soil organic carbon etc. Soil organic matter serves as the primary indicator of soil quality for scientists and farmers.
The subindicators of soil quality include: macro fauna, organic matter, physical quality, chemical quality and soil morphology which are the different aspect of soil quality.
Soil quality indicators can be measured by: (i) the traditional methods of laboratory analyses (ii) the Munsell soil color chart or (iii) proximal and remote sensing tools. These Indicators allow farmers to see what is happening in soil.
IMPORTANCE OF SOIL QUALITY ASSESSMENT
1. It is used to identify land areas that are problematic for use
2. Used to make realistic estimation of food production
3. Monitor changes in sustainability and environmental quality as related to environmental management
4. Use by government agencies to formulate land use policy
5. Used by government agencies to formulate sustainable agriculture
CATEGORIES OF SOIL INDICATORS
Soil quality indicators can be categorized into four groups
1. VISUAL INDICATORS
These are indicators that can be observed with the aid of the eye or use of photographic interpretation. Areas visualizer include exposed subsoil, soil colour change, ponds, runoff, plant respond, weed species etc are used to determine indicators.
2. PHYSICAL INDICATORS
This is related to the arrangement of soil particles and pore. This can be determined through porosity, top soil depth, aggregate stability, texture, bulk density, and compaction etc. These properties can have effect on root growth, infiltration, amount of water and its movement within pore space, seed emergence etc.
3. CHEMICAL INDICATORS
Chemical indicators carry out the following functios: they control solubility and mobility of heavy metals which are contaminants, they control the toxicity of heavy metals, they affect microbial activities, growth and diversity. They affect soil buffering capacity, and cation exchange capacity, water quality, buffering capacity, nutrient availability, and amount of microorganisms, etc.
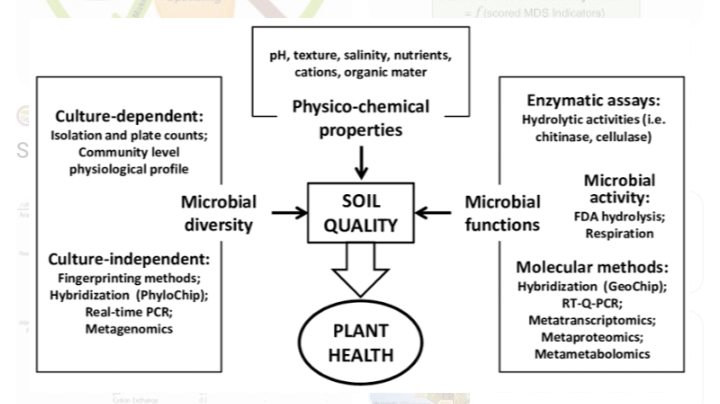
4. BIOLOGICAL INDICATORS
Soil organisms which are micro or macro organisms such as bacteria, fungi, nematodes, protozoan, beetles, earthworms, mites, rodents etc assist in the decomposition of soil organic matter, nutrient cycling, soil pollutant degradation, stability of soil structure, etc. They are referred to as soil biota.
To measure biological indicators, potential mineralizable nitrogen (PMN) , respiration, enzymes and POM are selected for measuring soil biota.
Respiration rate can be used to detect and measure the decomposition of organic matter.
A fungal byproduct called egosterol is used to measure activities of micro organism that assist in stabilising soil aggregates etc
FEATURES OR ATTRIBUTES OF SOIL QUALITY INDICES OR INDICATORS
1. They are easy to measure and interprete parameters
2. It is a rapid or less time consuming method
3. High sensitivity of parameters to detect differences on a temporal and spatial point scale
4. Repeatable methodology and reversible so that improvement and decay can be measured.
In conclusion, productivity and sustainability of any soil depend on the management practices and quality of the soil. Soils with good quality promotes high agricultural productivity and brings about a friendly environment.
Soil quality explain more on the physical attributes of soil. The physical attributes which include soil colour, complex soil characteristics such as soil organic matter, nutrient amounts, and soil structure, etc are all influenced by management practices and they enhance or diminish soil health.
.
