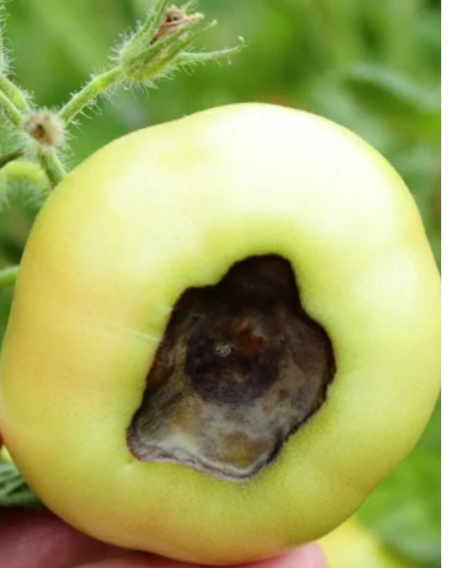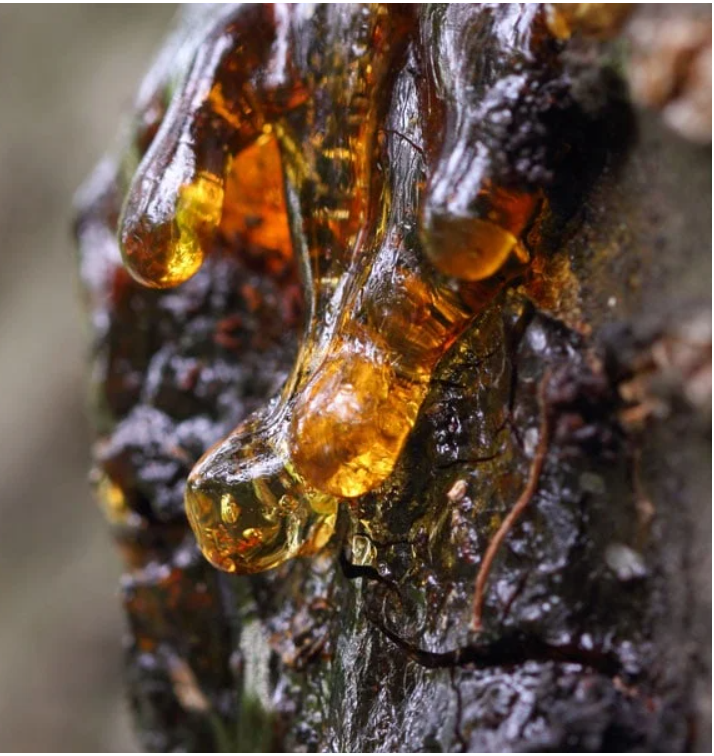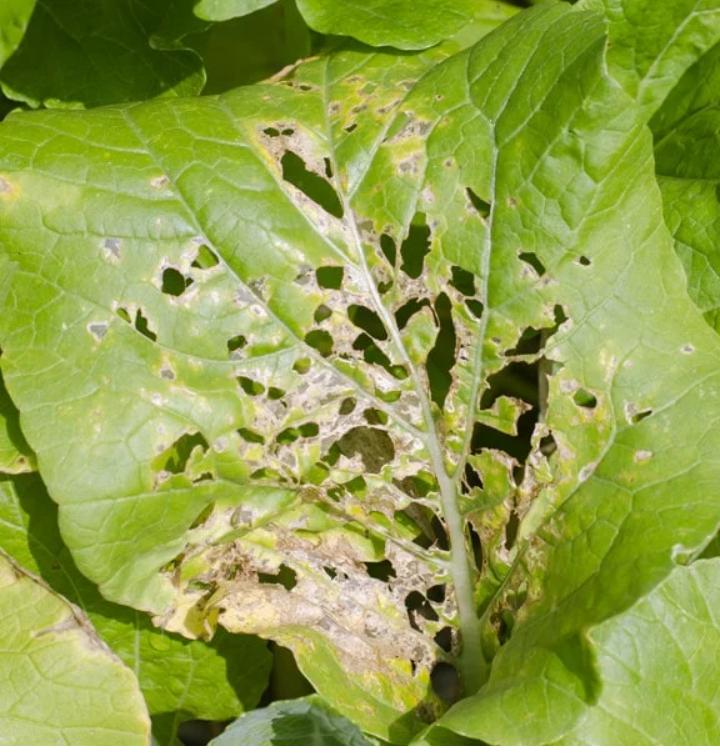
Disease of both crop and Livestock had constituted a major problem to farmers all over the world. Diseases had lead to general reduction in agricultural production over the years. All species of plants (wild and cultivated) are subject to disease.
In crop production, disease can cause total destruction of the crops if they are not Controlled. They are usually caused by pathogens resulting in physiological and anatomical abnormalities expressed in characteristic symptoms. Loss of crops from plant diseases may result in food insecurity.
FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR DISEASES
There are three factors responsible for diseases.
1. The pathogen
2. The host
3. The environment
Any reduction of any of the factors leads to a reduction of disease level.
1. HOST CONDITION: The plants at their different age stages are refer to as the host. A plant may be susceptible to a particular disease at different stages. For example, at maturity stage, Cocoa plant is susceptible to late blight and seedling blight at seedling stage.
SUSCEPTIBILITY : This is the degree to which a plant respond negatively to pathogens.
Factors that contribute to plant susceptibility to diseases are: insufficient nutrients and spacing between plants.
2. ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITION: This include temperature, wind, vectors carrying agents like insects, nutrient exudates on plant surfaces, chemical stimuli on wounds or natural openings in plants like stomata and lenticels etc
3. PATHOGENIC CONDITION: Pathogens can gain entry into plants through wounds made mechanically, vectors, fertilisation, through intact plants ( that is, plants without wounds but pathogens like fungi using it’s penetrating structure to gain entry into the plant)
EXAMPLES OF DISEASES THAT AFFECT PARTS OF PLANTS
1. Leaves: powdery mildew, rust, necrotic spots, Chlorosis lesions and blight
II. Roots and stems: rot and damping off, Chlorosis
III. Fruits: white mildew, scabs, black knot, blossom End Rot etc.
CLASSIFICATION OF PLANT DISEASES
Plant Diseases may be classified based on their nature of their Causative agents. Infectious (biotic) and non infectious (abiotic) diseases.
INFECTIOUS DISEASES : These are diseases caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, mycoplasmas, higher plants, nematodes, and protozoan etc
NON INFECTIOUS DISEASES : These are diseases caused by nutrient deficiencies, soil acidity, soil alkalinity, mineral toxicity, air pollution, toxicity of pesticides, insufficient or excess of moisture or light, and low temperature etc. This can be controlled by manipulating the environmental conditions around the crop.
DISEASES OF CROPS

1. DISEASES OF CEREAL CROP.
a) DOWNY MILDEW: It is a fungal disease caused by Peronosclerospora sorghi on maize and sorghum, Sclerospora gramunicola on millet and Erysiphe gramunis on wheat.
Symptoms
-chlorotic streak on leaves
-necrosis
– retarded growth
Control
-destroy infected plants immediately
-In maize, early planting is recommended
– treat seed with fungicides
-plant resistant varieties
2.RUST: It is a fungal disease caused by basidiomycetes. It affect crops like sugar cane, maize, millet etc. Puccinia saccharin on sugarcane, Puccinia polysora on maize and Puccinia penniseti on millet. It is one of the most destructive plant disease that affect leaves, stems and flowers
Symptoms
-rusty brown pustules on leaf surface
-chlorotic leaves
Control
-plant resistant varieties
3. SMUT: It is a fungal disease caused by basidiomycetes. It affect maize and sorghum. Sphaceiotheca reiliana on maize and Sphaceiotheca sorghi on sorghum.
Control:
-treat seeds with fungicides
-plant resistant varieties
4. Streak virus disease
It is a viral disease transmitted by leafhopper (Cicadulina spp). It infest maize plant.
Symptoms
-narrow chlorotic streaks along leaf veins
Control
-plant resistant varieties
Other diseases of cereals are blast disease of rice, blight, honeydew disease, leaf spot, anthracnose, nematode diseases.
DISEASES OF LEGUMES
1. ANTHRACNOSE : it is a fungal disease caused by Collectrichum hindermuthianum. It affect cowpea, and other legumes
Symptoms
-lesion on seeds
– pod loss
– purple brown discoloration of petiole, leaf veins and stem
– it usually infect the aerial parts of the plants
Control
-Crop rotation
-plant resistant varieties
-treat seed with fungicides
2.BLIGHT: It is a fungal disease that affect cowpea. It is caused by Corticium solani, and Sclerotium roffsii
Symptoms
-red brown spot on leaves
-lesions on leaves and stem
Control
-avoid overcrowded planting
-avoid sowing in the rain
– plant resistant varieties
3. GROUND NUT ROSTETTE DISEASE
it is a viral disease transmitted by aphids
Symptoms
-chlorotic leaves with mottled appearance
-pale yellow mosaic on veins and stems
– reduced flower and nut formation
Control
– early planting
-close spacing when planting
-destruction of alternative host
4. LEAF AND POD SPOT:
It is caused by Ascochyta pisi on peas. The disease is both soil and seed borne.
Symptoms
-leaves shrivels and dry
Control
-seed dressing
-crop rotation
Other diseases of legumes include fusarium wilt, rust, downy mildew, virus diseases, leaf spot of ground nuts, and nematode diseases etc.
DISEASES OF ROOT AND TUBER CROPS
1. ANTHRACNOSE: It is a fungal disease caused by Collectrichum gloeosporioides. It infect cassava (Manihotis).
Symptoms
– dark brown to black lesions on leaves, petiole and stems
-canker
Control
-plant resistant varieties
-practice mixed cropping
-staking
-crop rotation
2. CASSAVA MOSAIC VIRUS
it is caused by a vector called white fly (Bemisia tabaci).
Symptoms
-mosaic pattern on leaves,
– puckering, distortion and reduced leaves
Control
– plant resistant varieties
-Quarantine
-manipulation of planting date
-sanitation
3. ROT: This is a disease of sweet potato, cocoyam. It is a fungal disease caused by Ceratocystis fimbriata. It infect the roots and tubers.
Symptoms
-sunken black lesions
-brown necrotic lesions on roots.
-plant wilt
Control
-crop rotation
– avoid mono-cropping.
Other diseases of roots and tubers are blight, leaf spots, and nematode diseases
5. Diseases of vegetable crops : blight, damping off, leaf spot, virus diseases, and bacterial diseases etc.
PLANT DISEASE MANAGEMENT
Disease management begins with accurate diagnosis.
PLANT DISEASE DIAGNOSIS: It is possible to diagnose plant disease by visualising the symptoms alone. But to determine whether the disease is caused by infectious agents or not, detailed site, plant information and laboratory analysis are required. To diagnose a plant disease, plant samples must be collected from the field and analysed in the diagnostic laboratory after which the disease can be identify and managed
The best management practices is to avoid the diseases before their outbreak. Disease Prevention on the other hand is not always possible.
There are some principles to adhere to in disease management. This disease management principles include:
1. Exclusion : preventing pathogen introduction to areas where they do not currently exist
2. Avoidance : to inhibit establishment of pathogens that exist in other areas.
3. Resistance : selecting plants with increase tolerance to pathogens
4. Protection : steps taken to protect plants form infections
5. Eradication : limiting pathogen spread once a plant is infected
The most important plant disease management practice is sanitation.
TERMINOLOGIES
PATHOGENS : These are disease inducing organisms which passes through a regular cycle of development and reproduction
PHYSIOLOGICAL FACTORS: These are inanimate objects which may be physical, chemical and or environmental factors which are essential for normal growth of plants but when deficient or in excess lead to diseases. Examples are water, heat, inorganic salts.
CHLOROSIS : yellowish colouration of green plant parts due to failure of chlorophyll formation or destruction
LESION: This is a viral disease symptom showing intermingled patches of green parts of plants
DAMPING OFF: Destruction of seedlings close to parts near the soil which result to falling over or decay of seeds in soil
DOWNY MILDEW: This is a fungi spore growing on the lower surface of leaves, stems and fruits or on upper surface of leaves
PUSTULE: Small raised blisters on plants epidermis as a result of emerging spores of disease agents
NECROSIS: process of killing (death) plant tissues.
BLIGHT: rapid discoloration, wilting and death of plant tissues

BLOTCH: Large spot on leaves, shoot or fruits
BRONZING: leaves or needles turn bronze in colour
DIEBACK: Progressive death of shoots, branches or roots starting from the tip.
WILTING : drooping of leaves or other plant parts
MOSAIC : non uniform foliage coloration. Normally intermingling of green colour and yellow patches
MOTTLE: irregular pattern of light and dark area on plant.
ROT: decomposition and destruction of tissues

RUSSET: yellowish brown or reddish brown scar tissues on a fruit surface
SCAB: crust-like disease lesion
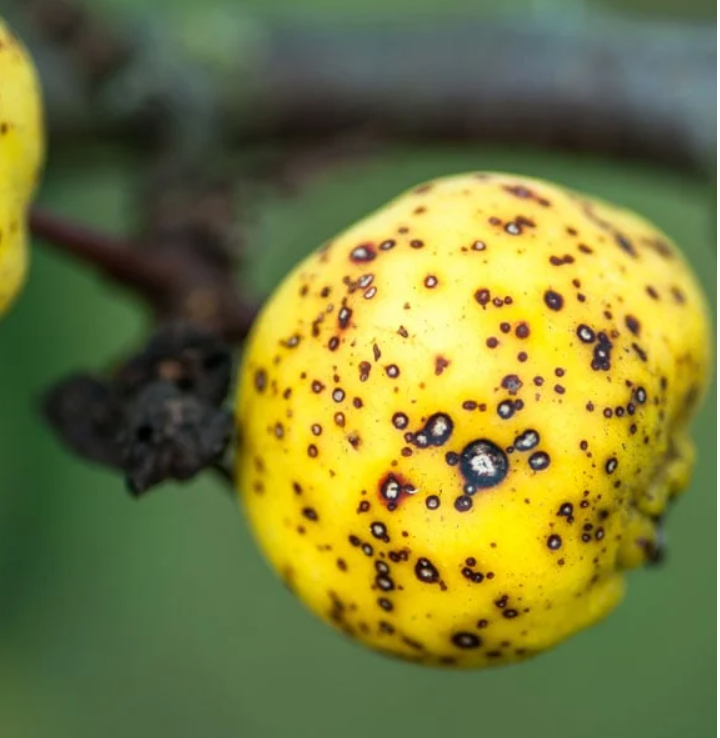

RING SPOT: lesion with a dark outer ring and lighter center
SCORCH: browning and necrosis of leaf marging

STUNTING: reduced growth of a plant, where plant or plant parts are smaller than normal
GALL : abnormal, localised swelling on leaf, stem and root tissues
GUMMOSIS: production of sticky gum that is extruded by the plant
LEAF SPOT: lesion on a leaf, which may vary in size, colour and shape.



