Conventional Agriculture had been seen as a way of improving the quality and quantity of Agricultural produce from both crops and Livestock. The use of agrochemicals like synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, antibiotics, vaccines, etc on both crops and Livestock, and genetically modified organisms had being a sustainable way of achieving better yield by farmers. But conventional farming methods come with a host of problems including health-related diseases like cancer, pollution, degradation of soil and water, and impact on domestic animals. Soil health had being hampered, . Residual effect of chemical fertilizers had affected the soil, human and Livestock. Pests now develop resistance to the chemicals being used on them and a host of other problems had emerged from conventional farming. Therefore, Organic farming came to being.
Organic farming is defined as production of crop, animal, and other products without the use of synthetic chemical fertilizers and pesticides, transgenic species, or antibiotics and growth-enhancing steroids, or other chemicals.
From: Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment, 2005.
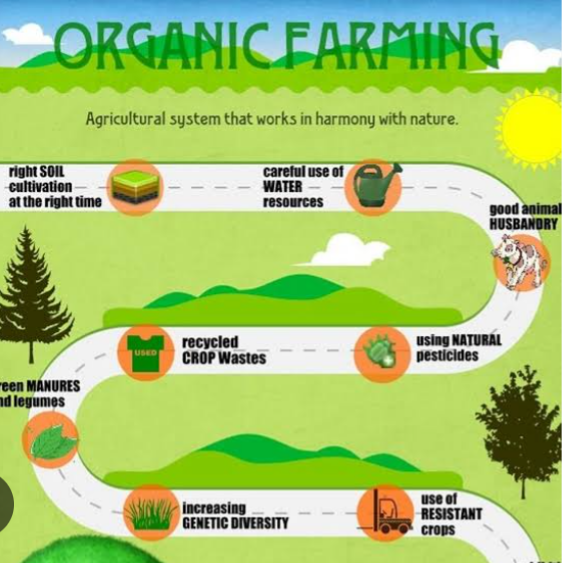
Organic farming relies on the use of ecologically balanced agricultural principles like crop rotation, cover cropping, green manure, organic waste, animal by-products, such as feather meal or blood meal as fertilizers, biological pest control, mineral and rock additives, natural pesticides and fertilizers which are not made from chemicals etc.
Nowadays, agrochemicals are believed to be contaminants to individual health and the environment. It causes a decrease in soil fertility, decrease in plant vitality and immunity, decrease in biodiversity, pollution of the environment and lower the quality of food consumable by human and livestock.
Organic farming is an alternative to conventional agricultural.
IFOAM – Organics International (formerly known as the International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements) is a worldwide organization advocating for organics, with over 700 affiliates in more than 100 countries all over the world.
The International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movement (IFOAM), an international organization established in 1972 for organic farming organizations defines the goal of organic farming as:
Organic agriculture is a production system that sustains the health of soils, ecosystems and people. It relies on ecological processes, biodiversity and cycles adapted to local conditions, rather than the use of inputs with adverse effects. Organic agriculture combines tradition, innovation and science to benefit the shared environment and promote fair relationships and a good quality of life for all involved…”
Differences Between Organic and Conventional Farming Methods
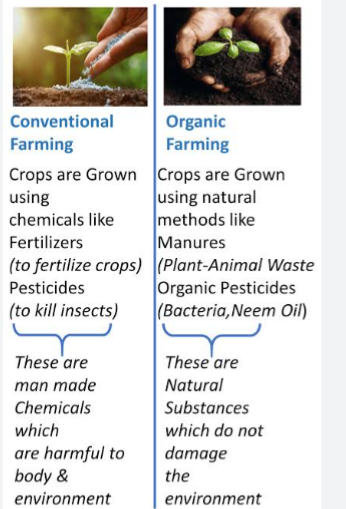
On the other side, the organic farmer
1. will prepare and enrich his land before sowing by sprinkling natural-based fertilizers such as manure, bone meal or shellfish fertilizer.
2. Mechanisation is practiced preferably chemicals are not used on the farm.
3. Farmer fertilize their farm using manure or compost made from animal dung or poultry droppings. The feed fed to the animals and birds must not contain chemical substances as the residue will be in their dung and droppings.
4. Seeds are treated with natural plant extracts before planting.
5. Weeds are eliminated using manual labor or flame weeder or use animals to eat away the weeds.
6. Animal diseases are prevented or treated using plant extracts
7. Preservatives and additives are not added to animal feeds
8. Plants and Livestock pests are treated using plant extracts and other natural means without chemicals.
9. Chlorinated and treated irritation water is not used. But organic farmer uses rain water etc.
BENEFITS OF ORGANIC FARMING
1. Harmful Pesticides are not used
Pesticides have harmful effects on the environment. Pesticides pollute and contaminate the soil, water and air. Therefore, organic farmers control pests through more natural methods like cover crops, use of plant extracts, composting and crop rotation.
2. Improve soil health
Healthy Produce comes from healthy soil. The soil can be healthy when crops produce yield at its maximum. That is, the soil is rich in organic matter, all macro and micro nutrient are enough and available for plant growth and yield.
Organic farmers therefore uses natural fertilizers on their soils before they plant crops. One of the primary ways they maintain healthy soil is by using compost, which contains many helpful bacteria that build up the ground. Other ways include the use of manures produced by plants and Livestock not fed with feeds containing chemicals
3. Reduces Erosion
Erosion deplete soil nutrients. Loose Soils and Soils without plant covers are prone to erosion. Cementing agents, organic matter and plant cover will reduce soil erosion. Use of chemical fertilizers with open land surface, thus, causes erosion.
4. Limits Non-Renewable Energy Use
Non-organic farming practices contribute to climate change. In each step of the process from farm to fork, greenhouse gases are likely emitted into the atmosphere. The fertilizers used directly put off emissions, the equipment used to plant and harvest crops rely on fossil fuels, and agricultural animals eat food that contributes to climate change.
In organic agriculture, non-renewable energy sources are highly regulated. Plus, it slows climate change by reducing carbon emissions.
5. Discourages Algae Blooms
Algae are good source of food to fishes especially those raised in ponds. Algal blooms can also be harmful to the environment. They can affect the health of humans and the life in the water. They do occur when runoff water carry chemicals and fertilizers into nearby streams and rivers. They reduce the dissolved oxygen in water and light penetration to water depth.
Organic farming does not make use of chemical fertilizers which cause algae blooms.
6. Stimulates Biodiversity
The more diversity on a farm, the better — and organic farmers understand this principle. With more biodiversity, the farm is more stable and can ward off invasive species. A mixture of plants, animals and microorganisms promotes soil and animal health as well. This is because they can work together to prevent disease and erosion, which eradicates the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
7. Environment-friendly. It does not cause harm to the environment as natural inputs are made use off.
8. Healthy and tasty food.
Organic food has more nutritional values. They are more tasty and good for health. They have a longer shelf life than chemically grown food. Foods from organic farms are rich in nutrients such as vitamins, enzymes, minerals and other micro-nutrients compared to those from conventional farms.
9. It uses organic inputs.: Organic inputs that are of natural sources such as livestock dung and droppings, plant extracts, seeds, rain water, etc are used in organic farming.
10. Source of employment. Organic farming is more labour intensive. Labourers are needed in handling the inputs needed on the farm. Hence, it generates more employment
11. Uses sustainable practices. Little is needed to be invested in organic farming. Practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, manuring, and use of plant extracts to control pests etc are use. Less capital is used and a safer environment emerges.
CERTIFICATION OF FARMERS AND THEIR ORGANIC PRODUCTS.
Farmers must be certified for their produce and products to be labeled “organic,” and there are specific organic standards for crops, animals, and wild-crafted products and for the processing of agricultural products
In developed nations like EU and U. S, Organic produce and product certification had grained a lot of popularity with organic inspectors put in place to ensure that organic foods are made available to their populace. The populace have the right to chose what suit their taste in terms of organic and non organic produce and products. In the EU, organic certification and inspection is carried out by approved organic control bodies according to EU standards. Organic farming has been defined by the National Organic Standards of the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) since 2000, and there are many accredited organic certifiers across the country.
In developing countries like Nigeria, regard for organic food is not of priority to the populace as organic regulatory bodies and inspectors are still trying to gain a strong foothold in the country. What will satisfy the populace daily food need is of priority as the country still wallow in abject poverty.
Higher institutions like University of Ibadan where the Nigerian Organic Agriculture Network (NOAN) a non governmental organisation created in 2008 by consensus of stakeholders of organic agriculture sector in Nigeria has her Secretariat serves as an umbrella body for all stakeholders involve in organic Agriculture in Nigeria such as farmers, students, lecturers, Agronomist, non governmental associations and other professional bodies members. The activities of NOAN is hinged on four thematic areas:
- Advocacy
- capacity building
- Standards and certification
- Marketing
And their vision is to improve the quality of urban and rural livelihood through the adoption of organic Agriculture in Nigeria. They train and make known to the nation on the relevance of organic Agriculture and organic products certification.
Principles of Organic Farming

1. Principle of Health
Organic agriculture must contribute to the health and well being of soil, plants, animals, humans and the earth. It is the sustenance of mental, physical, ecological and social well being. For instance, it provides pollution and chemical-free, nutritious food items for humans.
2. Principle of Fairness
Fairness is evident in maintaining equity and justice of the shared planet both among humans and other living beings. Organic farming provides good quality of life and helps in reducing poverty. Natural resources must be judiciously used and preserved for future generations.
3. Principle of Ecological Balance
Organic farming must be modeled on living ecological systems. Organic farming methods must fit the ecological balances and cycles in nature.
4. Principle of Care
Organic agriculture should be practiced in a careful and responsible manner to benefit the present and future generations and the environment.
As opposed to modern and conventional agricultural methods, organic farming does not depend on synthetic chemicals. It utilizes natural, biological methods to build up soil fertility such as microbial activity boosting plant nutrition.
Secondly, multiple cropping practiced in organic farming boosts biodiversity which enhances productivity and resilience and contributes to a healthy farming system. Conventional farming systems use mono-cropping that destroys soil fertility.
Organic farming methods
1. Fertilizers
Compost
Building of organic matter in the soil is a priority for organic farmers . Organic matter can be built up through the application of manure, compost, and animal by-products, such as feather meal or blood meal. These materials need to decompose and make the nutrients in them available to crops through the activities of microbes. Due to the facts that some of these microbes are human pathogens, the USDA and National Organic Standards mandate that raw manure must be applied no later than 90 or 120 days before harvest, depending on whether the harvested part of the crop is in contact with the ground. Composted manure that has been turned 5 times in 15 days and reached temperatures between 55 and 77.2 °C (131 and 171 °F) has no restrictions on application times. Compost helps to enrich soil nutrients, increase microbial activities in soil, distroy weeds, improve soil structure, soil porosity and Prevention of erosion etc
2. Farming practices:
Cover cropping : Planting and then tilling in cover crops will help protect the soil from erosion, leaching, and provide additional organic matter to the soil. The tilling in of nitrogen-fixing cover crops, such as mucuna, clover or alfalfa, also adds nitrogen to the soil. Cover crops are commonly planted to improve soil fertility.
Crop rotation: Rotating of crops helps improve soil fertility, control pests, add nitrogen and organic matter to the soil, and increase farmers income.
3. Pest control
Organic pesticides are derived from naturally occurring sources. These include living organisms such as the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis, which is used to control caterpillar pests, or plant derivatives such as pyrethrins (from the dried flower heads of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium) or neem oil (from the seeds of Azadirachta indica). Mineral-based inorganic pesticides such as sulfur and copper are also allowed.
Organic pest control integrates biological, cultural, and genetic controls to minimize pest damage. Biological control utilizes the use of natural enemies of pests, such as predatory insects (e.g., ladybugs) or parasitoids (e.g., certain wasps) to attack insect pests. Pest cycles can be disrupted with cultural controls, of which crop rotation is the most widely used. Also, plant breeders have developed technologies such as numerous resistant crop varieties that are resistant to specific pests.
4. Crop production
The use of polyculture, in which multiple crops are grown together can help reduce the need for chemical pesticides and fertilizers and generally improves soil quality. Another alternative is the use of crop rotation which can help improve soil productivity and lessen the need for agricultural chemicals for fertilization and pest control. The use of nitrogen-fixing cover crops, smother crops, and green manures can help restore lost soils nutrients and reduce erosion. Composting crop residues and other agricultural wastes helps recycle nutrients back to the farmland.
5. Animal agriculture
Livestock such as cattle, sheep and goats which are ruminants can help forage on grasses or crop residues to produce manure which can help increase soil productivity. The manure can be used to produce compost. Poultry fed with no chemical based feeds and water can produce droppings to enrich soil fertility. Also, animal by-products such as feather meal, blood meal can enrich in soil nutrients.
Animal pests and diseases should be treated with natural source of material to make the animal produce and products certifiable as organic products.
6. Water:
Water used for organic farming should be free of chemical such as chlorine and other chemical pollutants released into water. The residual effects of these chemicals in plant and animals and their produce renders such produce and products from them not organic. Rain water, underground water and water farmers know their sources are fit to be used in organic agriculture.
Chemical usage can renders any agricultural produce uncertifiable as organic produce and products. All truely organic products should be labelled organic without the populace having any bias mind of what they are consuming.