SNAIL FARMING
Heliculture (snail farming) is breeding of edible land snails for human or industrial consumption. SNAILRY is a place where edible snails are kept, and reared. Snails are invertebrates belonging to the phylum Molusca and class gastropoda. People eat both snail meat and eggs (white caviar). Each snail has female and male reproductive organs to procreate fertile eggs. Hence, reason for calling them Hermaphrodites. Snails are nocturnal animals that prefer dark moist places. This gives reason why they are seen during rainy season especially under leaf litters. They hibernate during dry season by producing a mucur membrane to cover the mouth of their shell till the next rainy season. Before they hibernate, they would have stored enough food and water in their system to survive the long spell of dryness. As the rain start, they brake loss the mucur membrane and become active again.
As for the nutritional benefits, snails are a vital source of calcium, phosphorus, iron, and protein. Also, snails are low in cholesterol, sodium, and fats.


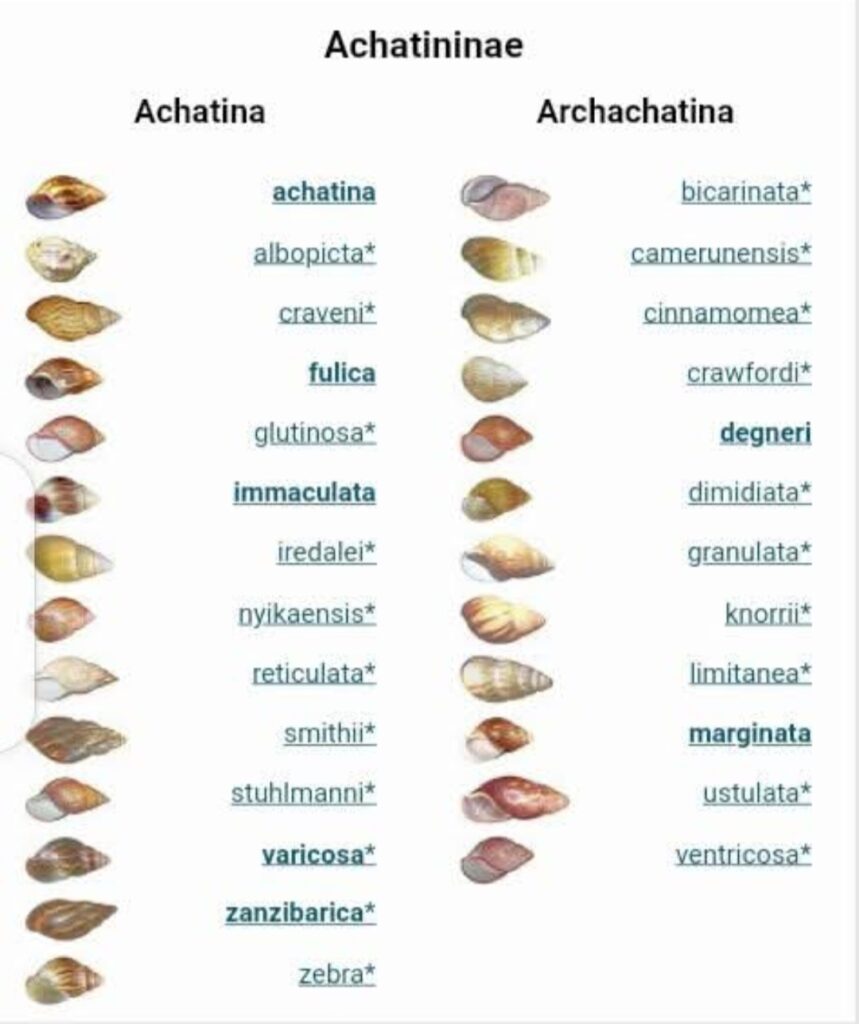
SPECIES OF SNAILS
There are more than 65,000 animal species belonging to the class Gastropoda. Among the more than 65,000 species of gastropods, about 30,000 are marine, 5,000 live in fresh water, and 30,000 live on land. In general, oceanic gastropods are most diverse in number of species and in variety of shell structures in tropical waters; several hundred species (each represented by a small number of individuals) can be found in a single coral reef habitat.
Gastropod is the largest group in the phylum Mollusca. The class is made up of the snails, which have a shell into which the animal can generally withdraw, and the slugs, which are snails whose shells have been reduced to an internal fragment or completely lost in the course of evolution. Other examples of these gastropods include: conch, periwinkles, abalone, limpets, and whelks etc.
SIZE RANGE AND DIVERSITY OF SNAIL SPECIES
Some adult marine snails (Homalogyra) and forest-litter snails (Stenopylis, Punctum) are less than one millimetre (0.04 inch) in diameter. At the other extreme, the largest land snail, the African Achatina achatina, forms a shell that is almost 20 centimetres (eight inches) long. The largest freshwater snails, Pomacea from South America, reach nearly 10 centimetres in diameter, and the largest marine snail, the Australian Syrinx aruanus, can grow to more than 0.6 metre (two feet). The longest snail probably is Parenteroxenos doglieli, a parasite in the body cavity of sea cucumber can grow to almost 130 centimetres (50 inches) in length, although it is only 0.5 centimetre (0.2 inch) in diameter. Most snails are much smaller, probably 90 percent of all adult snails are less than one inch in maximum dimension.
Land snails come in various species, colours, sizes, and shapes. There are three snail species in Nigeria. They are: Achatina fulica (the East African land snail), Achatina achatina (the giant Ghana or tiger snail) also called African land giant snail which is the most popular because of its economic size, and Archachatina marginata (the giant West African snail). Achatina achatina can lay up to 1,200 eggs yearly and is one of the largest snails in the world.
The Helix aspersa is a popular snail specie in Europe. Other species are the Burgundy snail (Helix pomatia), the garden snail (Cornu aspersum), the white garden snail (Theba pisana), and the milk snail (Otala lacteal).
BENEFITS OF SNAIL FARMING IN NIGERIA
1. Snail farming is a source of employment for people especially fresh graduates seeking for jobs. People can also set it up as per time jobs.
2. It requires little land or space to set up. 3. Snail farming has low start-up capital and maintenance costs. Forty snails consume about 2 kg of snail feeds (a mixture of crushed corn, chalk, milk powder, and herbs).
4. Snail meat and eggs are highly protenious and very profitable. Snail meat demand is high in the dry season.
5. Snails are environment-friendly because neither the snails nor their droppings have an offensive smell.
6. Snail is more nutritious than chicken meat, for it does not contain fat and cholesterol.
7. Snails are used in phermacautical and cosmetics industries
8. Snails are a rich source of proteins, iron, calcium, Vitamin A, and more minerals. Vitamin A boosts your immune system and strengthens your eyes.
9. Snail manure improved the organic content of the soil.
10. The snail mucin is important to a human’s skin. It hydrates the skin and treats dry skin conditions.
11. The snail mucin slows ageing and eliminates wrinkles, scars, and stretch marks.
12. An integrated farming system is very feasible with snail production. You can do snail-banana-earthworm-rabbit-palm tree and plantain farming.
13. Snail shells serve as calcium used for animal feeds.
14. Snails have a low mortality rate because they can live up to 20 years.
15. Snail shell can be crushed and used for scrubbing pots.
16. The shells of some species are used as ornaments or in making jewelry.
17. Some gastropods are scavengers, feed on dead plant or animal matter, to eliminate them from the surroundings. The animal and plant matter are converted to substances that can be used by plants to manufacture new organic compounds. In both field and forest, as in ponds, rivers, and oceans, gastropods are an important part of the decomposer community, and some are significant predators.
18. Some are predators; some are herbivores, feeding on algae or plant material; and a few species are external or internal parasites of other invertebrates.
19. Shells of certain snails are highly prized by collectors. The operculum of some Turbo species is used in making earrings; cameos are cut from the shell of the Red Sea snail Cassis rufa.
20. Abalone shells are used in many cultures for decorative purposes; the shell of the golden cowrie (Cypraea aurantium) served at one time as a badge of a chief in Fiji.
21. Strings of shells have been used as money.
NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF SNAILS
1. Serious medical problems are caused by the few freshwater snails (Pomatiopsis, Bulinus, Biomphalaria) that serve as intermediate hosts for flatworms that parasitize humans. Schistosomiasis is a disease caused by minute blood flukes (schistosomes). Both snails and flukes are most common in areas where fields are irrigated. Schistosomes also parasitize birds and mammals.
2. A skin rash called swimmer’s itch results from bird schistosomes, only partly successfully, to penetrate human skin. They die in the upper skin layers, and their decomposition causes local infection.
3. Other health problems are caused by several snails and slugs (e.g., Bradybaena, Angustipes, Veronicella) that serve as intermediate hosts for the rat lungworm. If an infected land snail or slug is inadvertently chopped up in a salad and eaten, the worm can migrate to the brain and encyst, causing moderate to severe damage.
4. In some places, introductions of Achatina and Helix have resulted in damage to crops and gardens by these rapidly multiplying snails.
LIFE CYCLE OF SNAIL
The life expectancy of snails in the wild is about 3 to 7 years, but in captivity, they can live up to 10-15 years or even more. Both aquatic and land snails have a three-stage life cycle: egg, larva, and adult. During their larval development stage, snails undergo a process known as torsion. Torsion occurs when a young snail’s mass (i.e., body and shell) shifts to one side, forcing the animal’s head and anus to be near each other. These larval snails have voracious appetites and may even ingest unhatched snail eggs when searching for food.
MANAGEMENT PRACTICES IN SNAILRY REARING.
FEEDING
To feed snails is less expensive because they feed on readily available food. For commercial purposes, food and water should be made available for the snails in the morning and night every day.
Snails can be fed with plantain, pumpkin, potato, lettuce, pawpaw, cabbage, banana, cucumber, etc. They also feed on flowers, vegetables, plantain and banana leaf, Pawpaw leaf, palm fruit, guava, oranges, watermelon and other fruits
Snails commonly feed on meal leftovers and green leaves without salt. Calcium is also vital for the growth of their shells. So ensure you add limestone, and egg shells to their feeds.
Other ideal staples for snail feeds include; corn, pap, beans, and rice, all without salt. Calcium is crucial in feeding snails because it boosts snails’ growth rate and produces thicker shells.
Compounded feeds can also be made and feed to them. Such feed must not have pepper or salt in them.
HOUSING
There are many ways of rearing snails. The most common places people keep snails in Nigeria are:
In a large room aquarium (it can be your garage).
In plastic or wooded snaileries (a place where edible snails are bred) on the balcony or compund.
In a greenhouse.
Outdoors on a farm (with simulated natural habitat) .
Use of car tyres
Locally, use of earthen pots.
The housing unit should be located under a shade not places with direct sunlight.
The size of the snails’ house will determine how comfortable the snails will be. Also, the style and size of the snail house are dependent on the size of your snail farm.
Snails house should be sorted according to their age. Separate them into mature, young, and newly hatched into the separate houses, and make sure the younger snails have a comfortable shelter that protects them from predators. Also, keep the temperature around and in the snailrys regulated and moist respectively. Use leaves to prevent dehydration in the snailery.
Fig 3: DIFFERENT SNAIL HOUSES
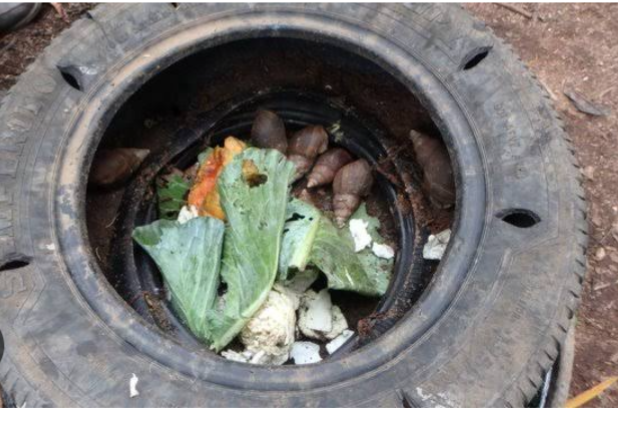
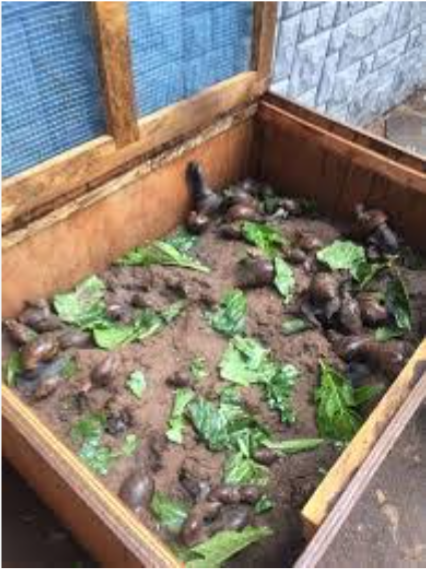



SOIL TYPE
The soil is the snails’ primary habitat, and is essential for their survival. Sandy-loamy soil is suitable because of the high level of organic matter it contains and ease of drainage when water is sprinkled on them. The soil also make it easy for snails to lay their eggs and drink water. Organic matter is also a source of food to them. For indoor farming or in a greenhouse, the soil should be 10 inches deep and kept moist. This will make it easy for the snails to burrow into the soil and lay their eggs.
PESTS AND DISEASES
Common predators of snails include; turkeys, geese, chickens, ants, snakes, lizards, and termites. Snails are not associated with many diseases, but it is common to find issues of bacteria and fungi due to overcrowded pens.
Toads, frogs, birds, weasels, skunks, moles, mice, and rats are carriers of fungi, nematodes, and fungi. Therefore, the housing unit should be properly protected.
REPRODUCTION IN SNAILS
Snails are hermaphrodites. A single snail possesses both male and female reproductive organs but they still require another snail of their kind to reproduce.
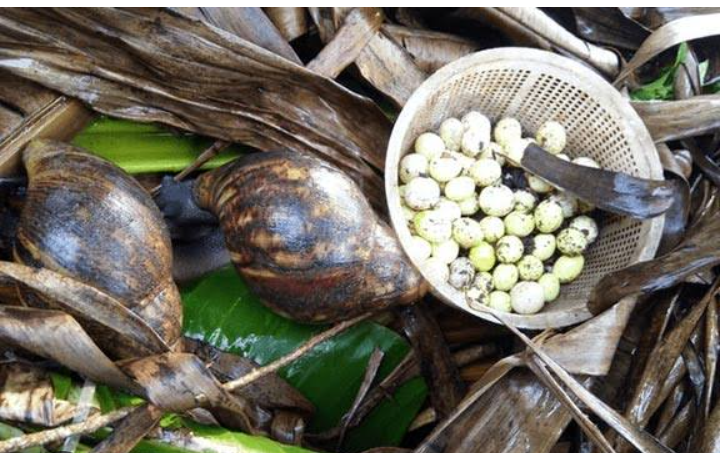
When snails are sexually mature – between 8 to 12 months, they mate. They would lay eggs in the soil that would hatch within a month.
The newly hatched snails would stay in the soil and feed on the egg shells. This would supply them the needed calcium to develop their own shell. After a week, they begin to emerge from the soil. Therefore, they should be separated into a new pen with adequate spacing and protection.
If left with adult snails, they would be eaten up.
Another alternative is to scoop the soil gently to evacuate the eggs to a new pen and cover with soil. Water should be sprinkled on the soil to keep it moist especially during dry season before the eggs hatch.
For commercial farming, where water supply is available to keep the snailery moist, there is no specific breeding period for snails, about 5 to 6 clutches of eggs would be produced per year with an average of 200 eggs,
This stage may be cumbersome, but the market value and fertile nature of the snails will compensate you for the long maturity period.

MARKETING SNAILS IN NIGERIA
Before starting snail rearing , carry out a market survey, analyze and test sales in the market. Determine the demand of people in different locations for snails and the market price. Some other major markets for snail meat are:
Supply snails to restaurants that prepare snails cuisines.
Sell snails to institutions with snail meat dishes on their menus (e.g. high-end schools).
Supply snails to events like weddings.
Sell them to food companies that sell packaged frozen snails or snail dishes.
Supply snails to companies that use them to make medications and beauty products/cosmetics.
Export to European and Asian countries
